Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2008; 14(25): 4087-4090
Published online Jul 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4087
Published online Jul 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4087
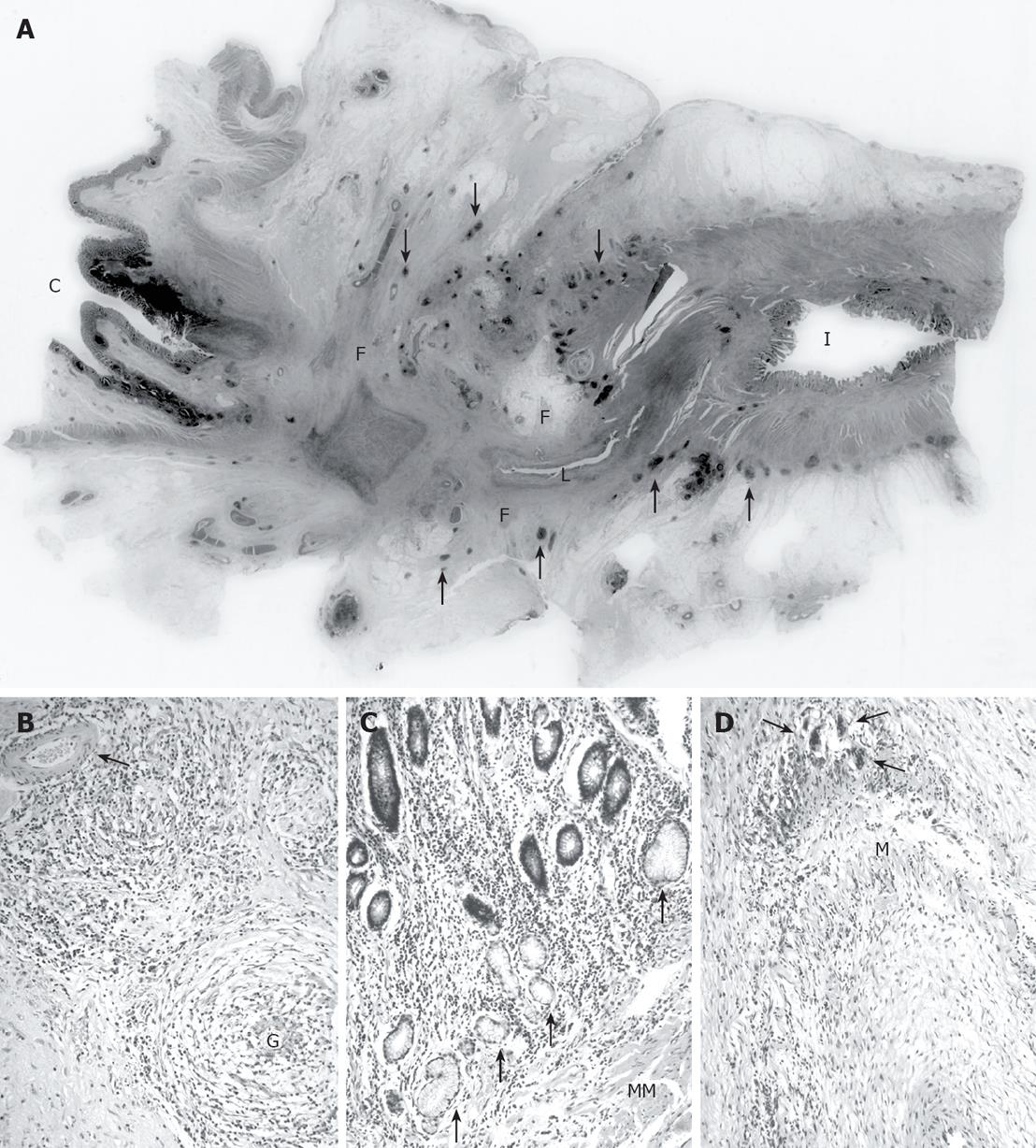
Figure 3 A: Whole histological mount of the terminal ileal stricture showing part of its stenosed lumen (L), with the caecum (C) and ileum (I) at either end.
The stricture showed transmural chronic inflammation (examples of the numerous lymphoid follicles are arrowed) with extensive fibrosis (F); B: Well-formed granulomas (G) with surrounding chronic inflammation in the subserosal tissues around the stricture with no vasculitis in an arrowed small muscular artery; C: Ileal mucosa proximal to the stricture showing extensive ulcer-associated cell lineage (arrowed) and chronic inflammation extending into the hypertrophied muscularis mucosae (MM); D: A medium-sized muscular artery within the fibrous tissue of the stricture showing chronic inflammation and multinucleated giant cells (arrowed) concentrated around the outer edge of the media (M) and the lumen of the artery in the bottom right corner.
- Citation: Farrant MA, Mason JC, Wong NA, Longman RJ. Takayasu’s arteritis following Crohn’s disease in a young woman: Any evidence for a common pathogenesis? World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(25): 4087-4090
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i25/4087.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.4087