Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2008; 14(24): 3819-3828
Published online Jun 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3819
Published online Jun 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3819
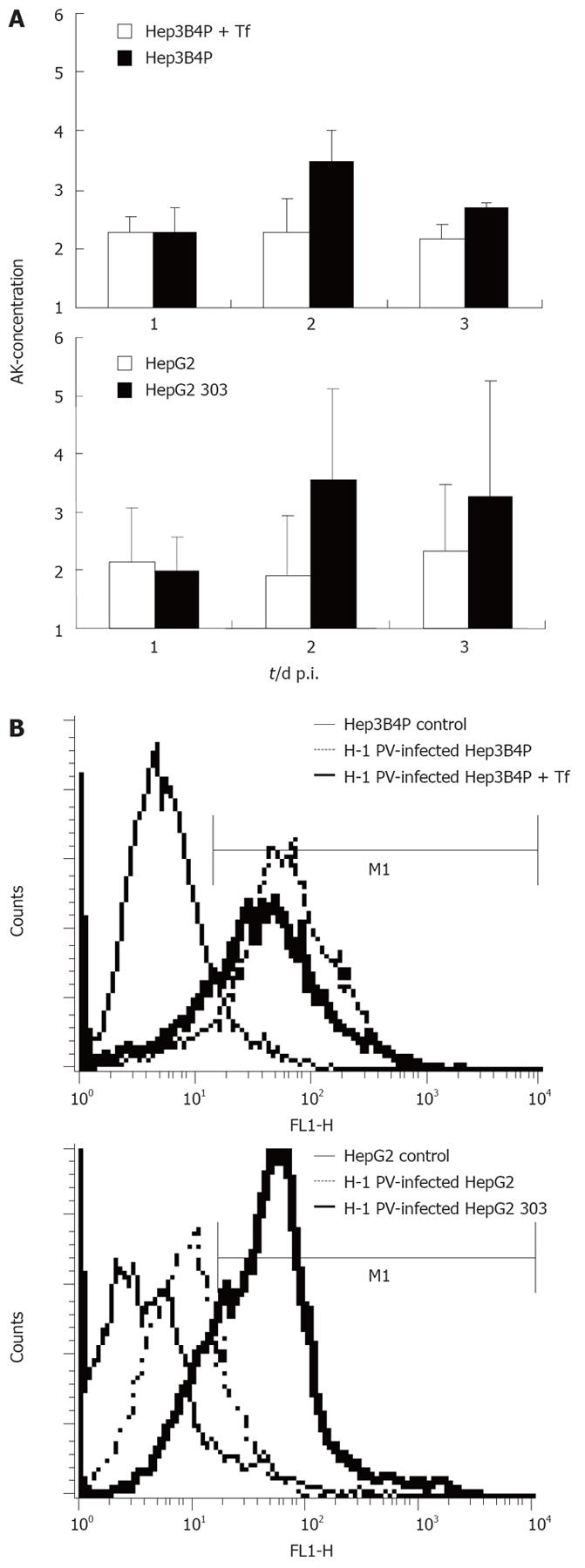
Figure 2 A: Cytotoxicity and induction of apoptosis in H-1 PV-infected p53 different tumor cell line pairs.
The early damage of tumor cells upon H-1 PV infection was measured with a standardized toxicity test via supernatant adenylate kinase (AK) concentration; B: Induction of apoptosis in H-1 PV-infected tumor cells is shown in histograms for annexin V (FL1-H) of Hep3B4P and HepG2 cells. Data are given as mean values of triplicates.
- Citation: Sieben M, Herzer K, Zeidler M, Heinrichs V, Leuchs B, Schuler M, Cornelis JJ, Galle PR, Rommelaere J, Moehler M. Killing of p53-deficient hepatoma cells by parvovirus H-1 and chemotherapeutics requires promyelocytic leukemia protein. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(24): 3819-3828
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i24/3819.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.3819