Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2008; 14(22): 3445-3451
Published online Jun 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3445
Published online Jun 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3445
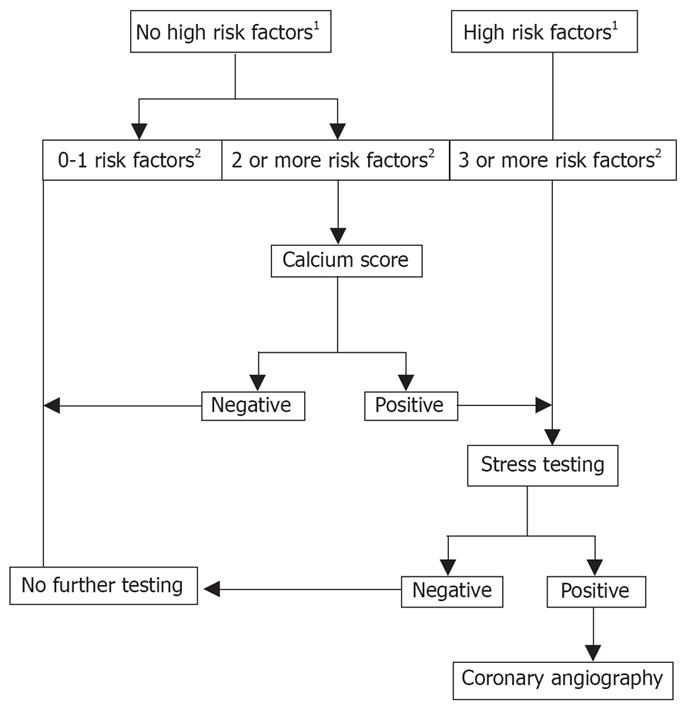
Figure 1 Algorithm for the diagnosis of ischemic heart disease.
There is no consensus on how to evaluate asymptomatic liver transplant recipients for the presence of CAD. However, a logical algorithm can be constructed using the current evidence from a limited number of outcome studies. The utility of this algorithm will require outcome testing to determine its sensitivity and specificity. In this approach, asymptomatic liver transplant recipients are divided according to the presence risk factors for CAD. Patients with 0-1 risk factor require no further evaluation. Those with 2 risk factors are first assessed by calcium scoring. If the score is zero, no further testing is required. If the test is not zero patients are referred for stress testing. Patients referred directly for stress testing include those with 3 or more risk factors and those with high risk factors. A positive stress test is an indication for coronary catheterization. 1High Risk Factors for CAD include diabetes, NASH, previous CAD, peripheral vascular disease; 2Risk Factors for CAD include age > 50 yr, hypertension, elevated cholesterol and obesity.
- Citation: Mandell MS, Lindenfeld J, Tsou MY, Zimmerman M. Cardiac evaluation of liver transplant candidates. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(22): 3445-3451
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i22/3445.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.3445