Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2008; 14(18): 2882-2887
Published online May 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2882
Published online May 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2882
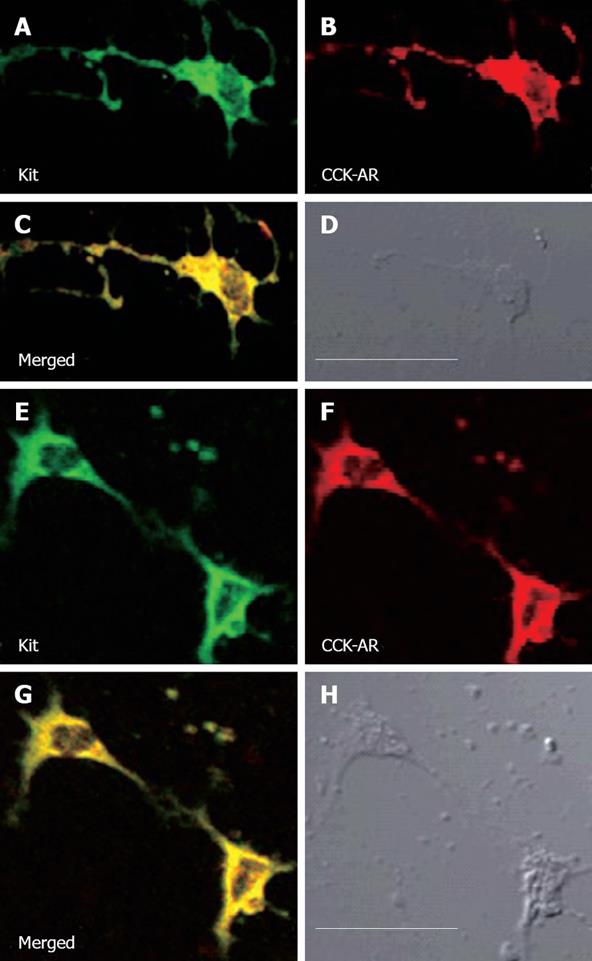
Figure 2 Colocalization of CCKAR immunoreactivity with markers for ICC, kit in guinea pig gallbladder cultured ICC.
CCK-AR immunoreactive ICC in the muscle of the gallbladder is distinctive of their labled processes. ICC possessed several processes (A-D); C-kit immunoreactive (green) ICC colocalize CCKAR (red); C: Compound micrographs from (A) and (B); D: Phase-contrast micrographs of the same gallbladder ICC at the same magnification; Often two or more labled ICC were aggregrated into a network (E-H), making it difficult to discern the individual cells; C-kit immunoreactive (green) ICCs colocalize CCKAR (red); G: Compound micrographs from (E) and (F); H: Phase-contrast micrographs of the same gallbladder ICCs at the same magnification; All these ICCs were big and had a large and angular nucleus; Bar (in D) 30 &mgr;m for (A-D) and (in (H)) 30 &mgr;m for (E-H).
- Citation: Xu D, Yu BP, Luo HS, Chen LD. Control of gallbladder contractions by cholecystokinin through cholecystokinin-A receptors on gallbladder interstitial cells of cajal. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(18): 2882-2887
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i18/2882.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.2882