Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2008; 14(18): 2810-2817
Published online May 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2810
Published online May 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2810
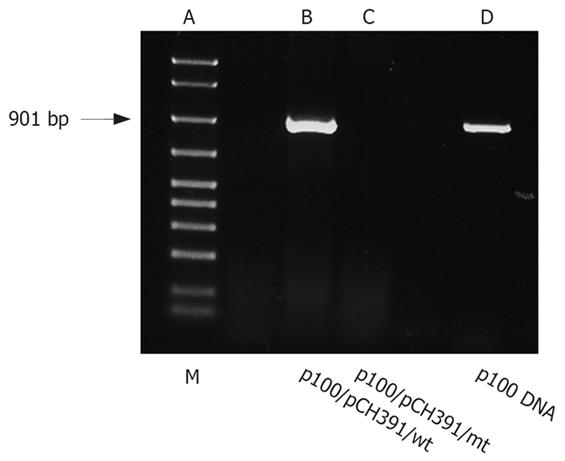
Figure 3 RT-PCR of genomic DNA from HepG2 cells transfected with a HBV polymerase expression plasmid.
7.5 &mgr;g p77 RNA mixed with 7.5 &mgr;g p92 β-Gal expression plasmid were transfected in each experiment as well as plasmids expressing either wild-type or mutant HBV polymerase (7.5 &mgr;g each). Genomic DNA was extracted and analyzed by non-denaturing 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. PCR fragments indicate the presence of toxin p77 cDNA. A: Bio-Rad marker 50-2000 base pairs; B: PCR amplified fragment of HepG2 cells cotransfected with pCH391wt and r100; C: PCR amplified fragment of HepG2 cells cotransfected with pCH391mt and r100; D: P77 DNA as control DNA.
- Citation: Hafkemeyer P, Brinkmann U, Brinkmann E, Pastan I, Blum HE, Baumert TF. Pseudomonas exotoxin antisense RNA selectively kills hepatitis B virus infected cells. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(18): 2810-2817
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i18/2810.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.2810