Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2007; 13(7): 1129-1134
Published online Feb 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i7.1129
Published online Feb 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i7.1129
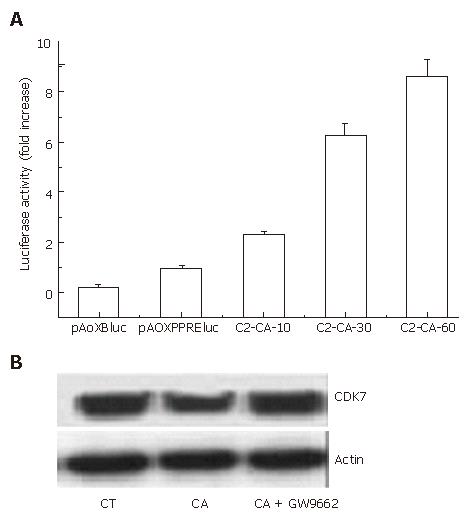
Figure 3 CDK7 and PPARγ pathways involved in cell cycle arrest induced by C2-ceramide.
A: activation of PPARγ transcriptional activity induced by C2-ceramide. Bel7402 cells were transiently transfected with the PPAR responsive element (PPRE) reporter construct (pAOXPPREluc) or the promoter-less control vector pAOXBluc following the treatment of different concentrations of C2-ceramide as indicated, PPARγ transcriptional activity was measured as described. The bar represents the relative fold increase of luciferase activity. The results show means ± SE (n = 3); B: C2-ceramide down-regulated the expression of CDK7, which was blocked by GW9662. Bel7402 cells were cultured with 30 μmol/L C2-ceramide in the presence or absence of GW9662, which was claimed as a specific PPARγ antagonist for 24 h. Total proteins were extracted and resolved on SDS-PAGE followed by Western blot assay using anti-CDK7 antibody. Data represents the results of three separate experiments.
- Citation: Wang J, Lv XW, Shi JP, Hu XS. Mechanisms involved in ceramide-induced cell cycle arrest in human hepatocarcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(7): 1129-1134
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i7/1129.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i7.1129