Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2007; 13(6): 964-969
Published online Feb 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i6.964
Published online Feb 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i6.964
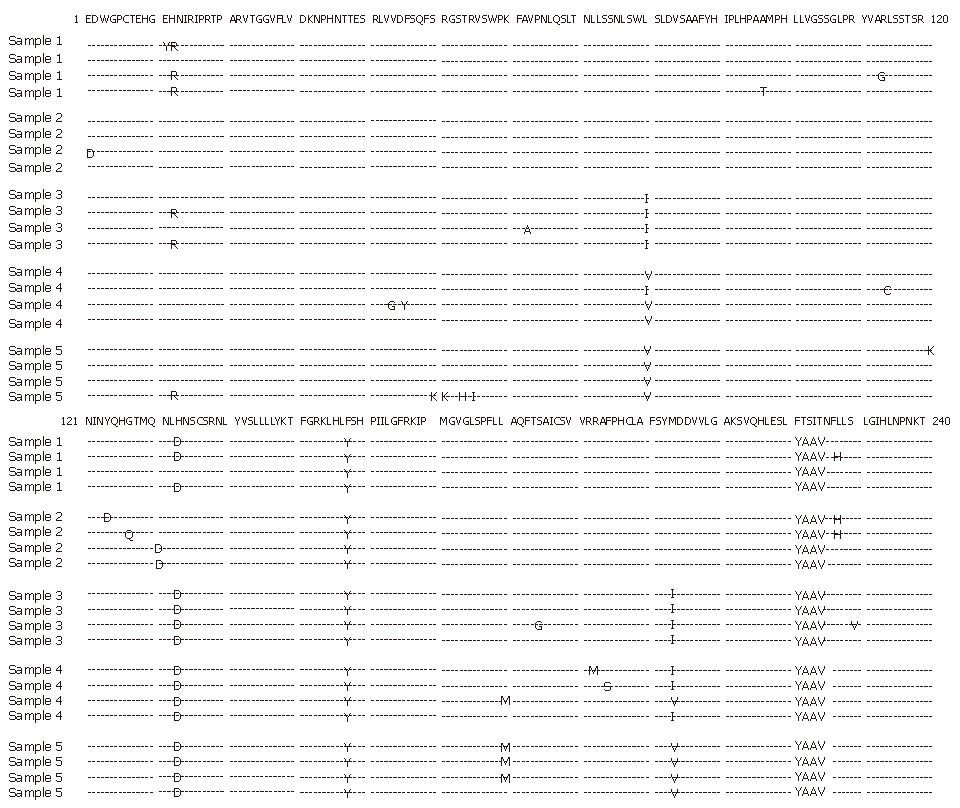
Figure 3 Comparison of amino acid sequences of HBV polymerase gene of isolates before lamivudine treatment (sample 1) and four sequential isolates (samples 2-5) during treatment.
A HBV mutant with substitutions of isoleucine for leucine at residue 80 (rtL80I) in combination with isoleucine for methionine at residue 204 (rtM204I) was observed 12 mo after treatment (sample 3). After vidarabine treatment, another HBV mutant with substitutions of valine for leucine at residue 80 (rtL80V) and valine for methionine at residue 204 (rtM204V) was observed (sample 4). These mutations predominated in combination with methionine for leucine at residue 180 (rtL180M) after interferon treatment (sample 5). The published HBV DNA sequence of hepatitis B virus variant (genotype C, AB033550, Okamoto et al) was used for comparison.
- Citation: Suzuki Y, Yotsuyanagi H, Okuse C, Nagase Y, Takahashi H, Moriya K, Suzuki M, Koike K, Iino S, Itoh F. Fatal liver failure caused by reactivation of lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(6): 964-969
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i6/964.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i6.964