Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2007; 13(43): 5707-5717
Published online Nov 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i43.5707
Published online Nov 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i43.5707
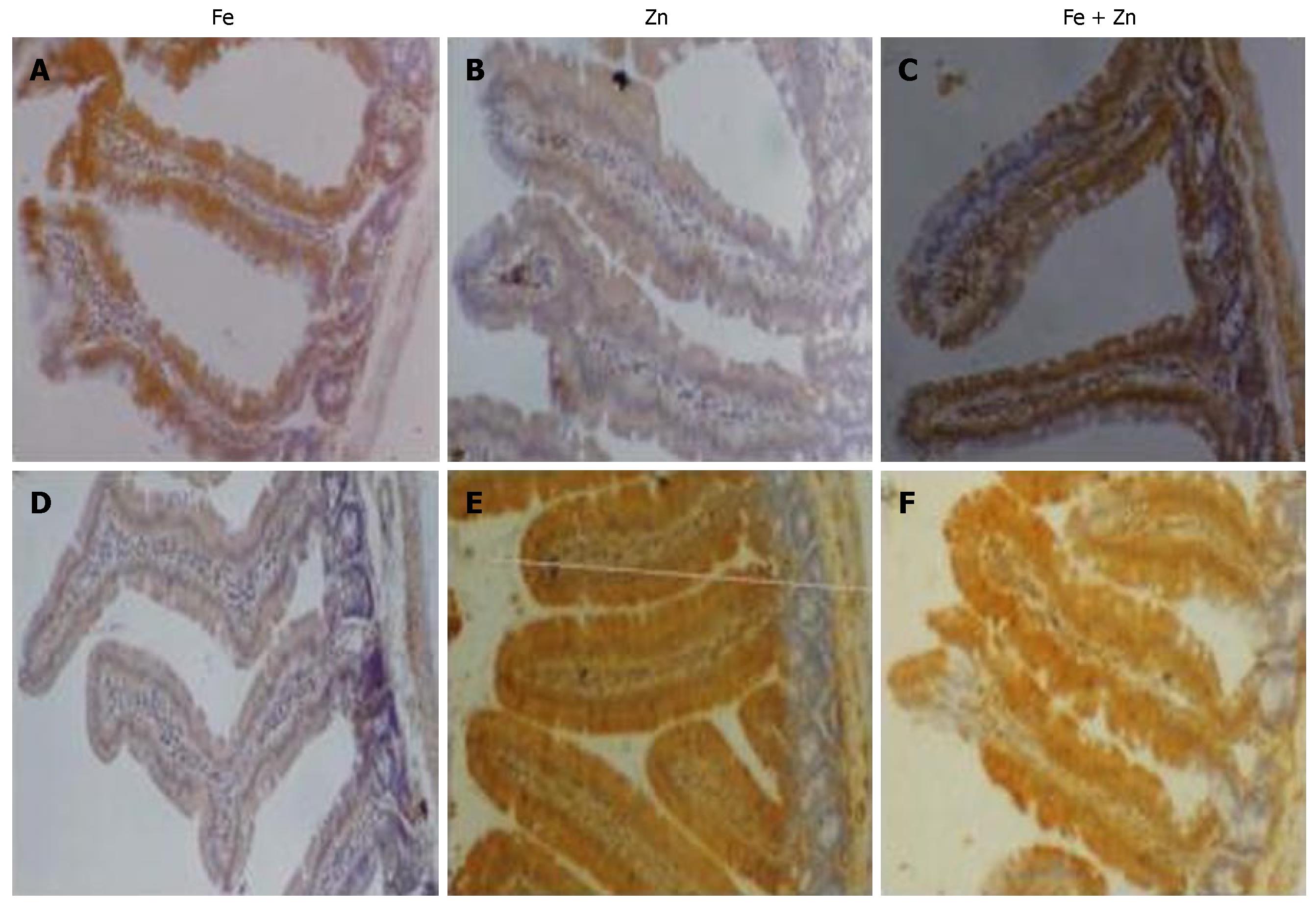
Figure 2 Zn reduces ferritin but enhances metallothionein abundance in the intestinal mucosa: A representative photomicrograph of the immunohistochemical localization of ferritin (top panel) and metallothionein (bottom panel) in the intestinal mucosa of Fe, Zn and Fe + Zn repleted groups.
The staining intensity indicates the abundance of ferritin and metallothionein (× 250).
- Citation: Bodiga S, Krishnapillai MN. Concurrent repletion of iron and zinc reduces intestinal oxidative damage in iron- and zinc-deficient rats. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(43): 5707-5717
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i43/5707.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i43.5707