Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2007; 13(43): 5707-5717
Published online Nov 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i43.5707
Published online Nov 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i43.5707
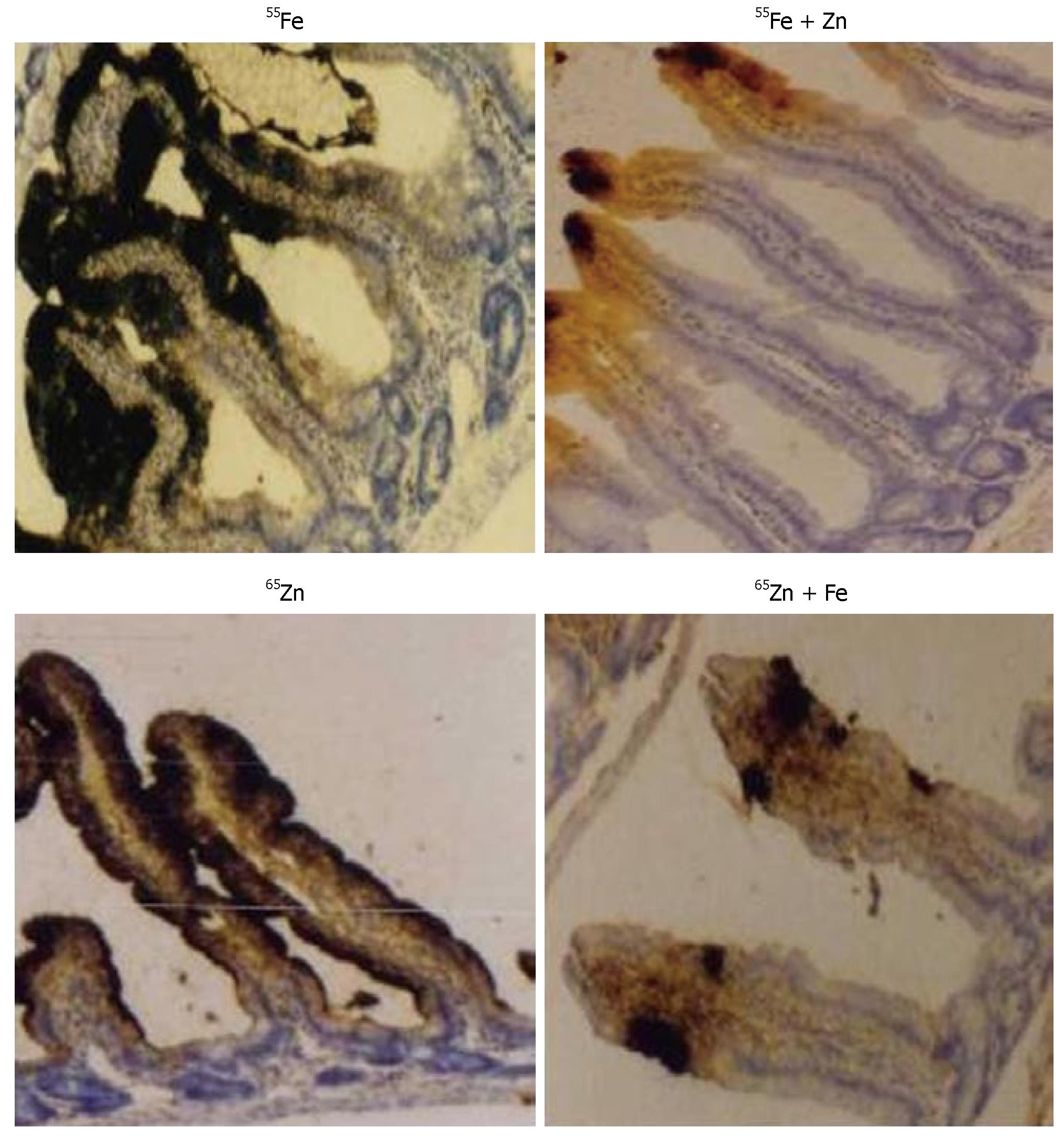
Figure 1 Zn reduces uptake of 55Fe and Fe reduces uptake of 65Zn during combined administration: A representative microautoradiogram of the duodenal mucosa of 55Fe in Fe (top left), Fe + Zn (top right), 65Zn in Zn (bottom left) and Fe + Zn (bottom right) groups.
Iron and zinc deficient rats were orally administered 37mBq of 55Fe and 4.0 mg Fe and/or 37mBq of 65Zn and 3.3 mg Zn. Presence of black spots in the intestinal mucosa indicates the presence of the radioactivity (× 100).
- Citation: Bodiga S, Krishnapillai MN. Concurrent repletion of iron and zinc reduces intestinal oxidative damage in iron- and zinc-deficient rats. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(43): 5707-5717
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i43/5707.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i43.5707