Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2007; 13(39): 5217-5225
Published online Oct 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i39.5217
Published online Oct 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i39.5217
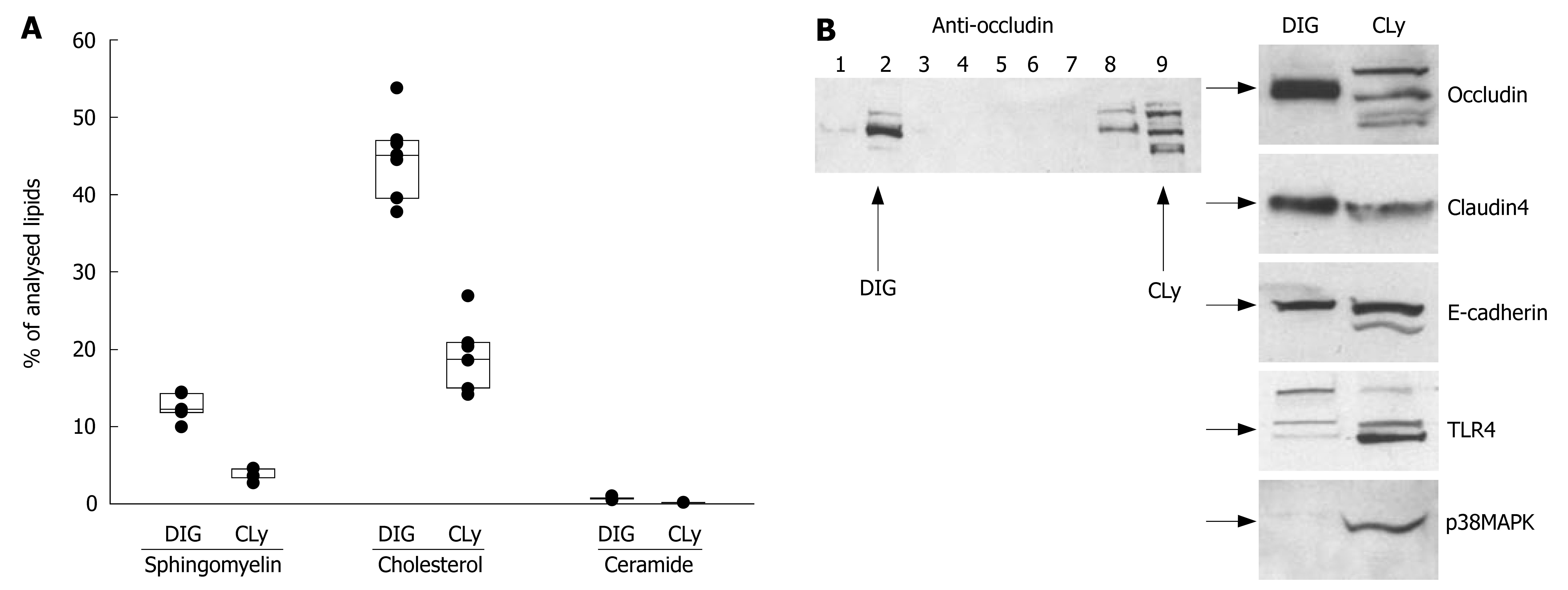
Figure 3 Preparations of detergent insensitive glycosphingolipid-enriched domains (DIGs) contain TJ-proteins.
A: Lipid analysis of DIGs from non-stimulated Caco-2 cells by tandem mass spectrometry revealed the presence of high amounts of sphingomyelin, cholesterol and ceramide when compared to the total cell lysate; B: Gradient fractions were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blot. Fraction No. 2 represents the raft-containing fraction at the 35%/5% interface (DIG); No. 9 represents the soluble fraction (cell lysate = CLy). The presence of high amounts of TJ-proteins occludin and claudin-4 and, to a lesser extent, E-cadherin show a clear association of TJ-proteins with DIGs. The simultaneous absence of other proteins like TLR4 and p38MAPK excludes significant contamination with non-raft fractions.
- Citation: Bock J, Liebisch G, Schweimer J, Schmitz G, Rogler G. Exogenous sphingomyelinase causes impaired intestinal epithelial barrier function. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(39): 5217-5225
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i39/5217.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i39.5217