Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2007; 13(38): 5108-5115
Published online Oct 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i38.5108
Published online Oct 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i38.5108
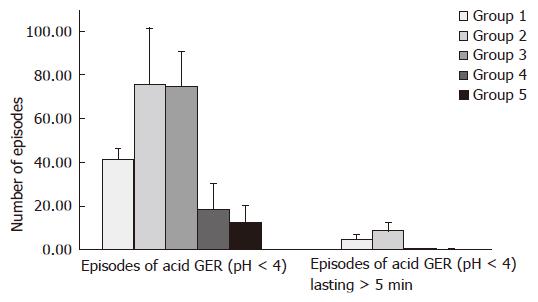
Figure 1 Summary analysis of number of episodes of acid GER (pH < 4) and episodes of acid GER (pH < 4) lasting > 5 min of 24-h pH-monitoring in 264 children suspected of GERD; pH-monitoring with 11- or 2-channel probe.
1Values of pH-monitoring parameters in group 1 did not undergo comparative analysis with corresponding values in remaining groups.
- Citation: Semeniuk J, Kaczmarski M. 24-hour esophageal pH-monitoring in children suspected of gastroesophageal reflux disease: Analysis of intraesophageal pH monitoring values recorded in distal and proximal channel at diagnosis. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(38): 5108-5115
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i38/5108.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i38.5108