Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2007; 13(37): 4931-4937
Published online Oct 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i37.4931
Published online Oct 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i37.4931
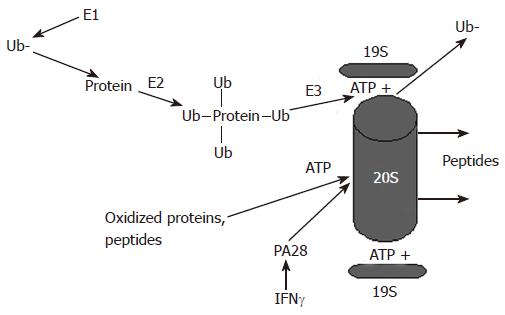
Figure 1 Proteasome-dependent degradation of proteins by the 26S and the 20S proteasome.
Proteins undergo ubiquitylation and are degraded in an ATP-dependent manner by the 26S proteasome, which activity is regulated by the 19S particle. Alternatively, oxidized proteins can be degraded by the 20S proteasome. This degradation is ATP-independent and is regulated by the 20S proteasome activator, PA28.
- Citation: Osna NA, Jr TMD. Implication of altered proteasome function in alcoholic liver injury. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(37): 4931-4937
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i37/4931.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i37.4931