Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2007; 13(35): 4761-4770
Published online Sep 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i35.4761
Published online Sep 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i35.4761
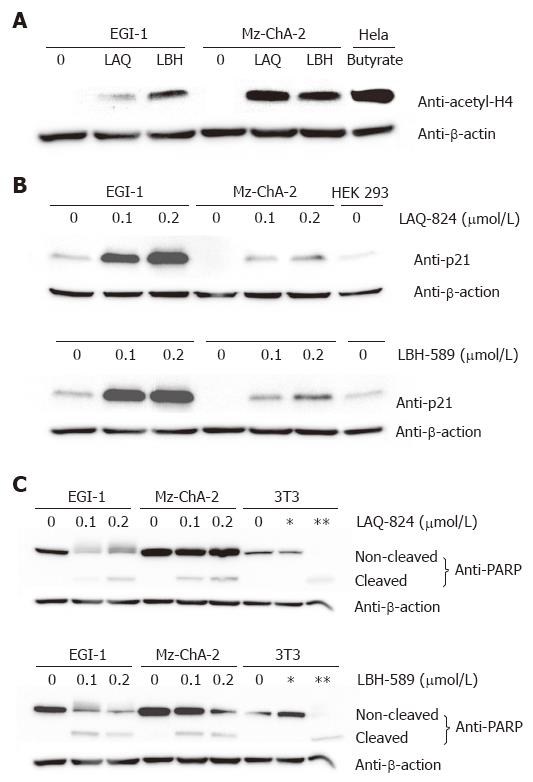
Figure 2 Mechanism of drug action after in vitro treatment with NVP-LAQ824 and NVP-LBH589 for 24 h.
Lane *: NIH-3T3 cells treated with 25 μmol/L etoposide for 5 h (negative control); lane **: NIH-3T3 cells treated with 10 μmol/L etoposide for 24 h (positive control). A: acetylation of histone H4; B: p21WAF-1/CIP-1 expression; C: PARP cleavage.
- Citation: Bluethner T, Niederhagen M, Caca K, Serr F, Witzigmann H, Moebius C, Mossner J, Wiedmann M. Inhibition of histone deacetylase for the treatment of biliary tract cancer: A new effective pharmacological approach. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(35): 4761-4770
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i35/4761.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i35.4761