Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2007; 13(31): 4207-4213
Published online Aug 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i31.4207
Published online Aug 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i31.4207
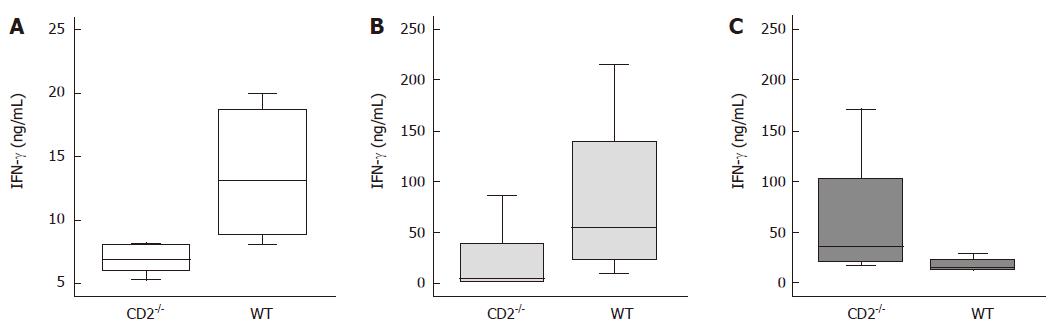
Figure 4 Decreased intestinal IFN-γ production in CD2-/- mice upon Toxoplasma gondii infection.
Production of IFN-γ by lymphocytes and concentration in sera obtained from CD2-/- or WT mice infected with the ME49 strain of T. gondii. Sera (A) and supernatants of stimulated mLN lymphocytes (B) of CD2-/- mice contain significantly less IFN-γ than appropriate probes of WT mice (P = 0.009, P = 0.039). Supernatants of stimulated splenocytes (C) of CD2-/- mice produce significantly more IFN-γ than appropriate cells of WT mice (P = 0.021).
-
Citation: Pawlowski NN, Struck D, Grollich K, Kühl AA, Zeitz M, Liesenfeld O, Hoffmann JC. CD2 deficiency partially prevents small bowel inflammation and improves parasite control in murine
Toxoplasma gondii infection. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(31): 4207-4213 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i31/4207.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i31.4207