Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2007; 13(31): 4177-4184
Published online Aug 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i31.4177
Published online Aug 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i31.4177
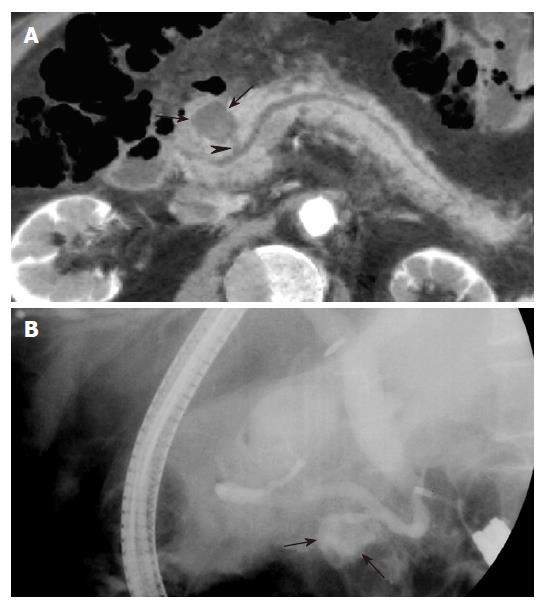
Figure 7 Pancreatic pseudocyst in a 64 years old man with epigastric pain.
A: MinIP (axial oblique 13.8 mm thickness slab) image shows a round cystic lesion (arrows) in the pancreatic head, communicating (arrowhead) with the pancreatic duct. This patient was diagnosed with pancreatitis on clinical and radiological findings (not shown); B: ERCP image obtained with the patient on the right lateral decubitus position shows the cystic lesion (arrows) filled with contrast material, which represents communication between the cyst and the pancreatic duct.
- Citation: Kim HC, Yang DM, Jin W, Ryu CW, Ryu JK, Park SI, Park SJ, Shin HC, Kim IY. Multiplanar reformations and minimum intensity projections using multi-detector row CT for assessing anomalies and disorders of the pancreaticobiliary tree. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(31): 4177-4184
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i31/4177.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i31.4177