Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2007; 13(31): 4177-4184
Published online Aug 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i31.4177
Published online Aug 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i31.4177
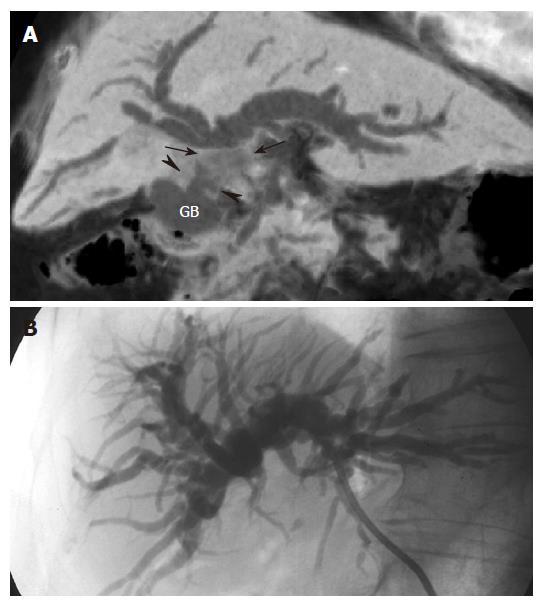
Figure 5 Extrinsic invasion of the common hepatic duct by gallbladder carcinoma in an 80 years old woman with jaundice.
A: MinIP (coronal oblique 14.3 mm thickness slab) image shows dilatation of the intrahepatic bile duct caused by an irregular mass (arrows) in the common hepatic duct, which is the result of direct invasion from the irregular wall thickening (arrowheads) of the gallbladder (GB). This image depicts well the relationship between gallbladder carcinoma and the obstructed biliary duct; B: PTC demonstrates only the biliary obstruction without any suggestion of the cause.
- Citation: Kim HC, Yang DM, Jin W, Ryu CW, Ryu JK, Park SI, Park SJ, Shin HC, Kim IY. Multiplanar reformations and minimum intensity projections using multi-detector row CT for assessing anomalies and disorders of the pancreaticobiliary tree. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(31): 4177-4184
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i31/4177.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i31.4177