Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2007; 13(31): 4177-4184
Published online Aug 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i31.4177
Published online Aug 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i31.4177
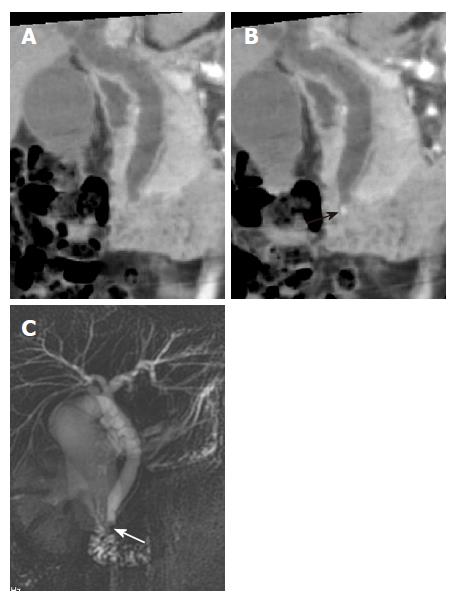
Figure 3 A small stone in the common bile duct of a 34-year-old woman with epigastric pain.
A: MinIP (coronal oblique 6.2 mm thickness slab) image shows mild dilatation of the extrahepatic bile duct without delineation of the stone; B: MinIP (coronal oblique 3.8 mm thickness slab) image with a slab thickness that is thinner than the size of the stone shows the stone (black arrow) in the distal common bile duct; C: MRCP demonstrates the low signal intensity of the stone (white arrow) in the distal common bile duct.
- Citation: Kim HC, Yang DM, Jin W, Ryu CW, Ryu JK, Park SI, Park SJ, Shin HC, Kim IY. Multiplanar reformations and minimum intensity projections using multi-detector row CT for assessing anomalies and disorders of the pancreaticobiliary tree. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(31): 4177-4184
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i31/4177.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i31.4177