Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2007; 13(30): 4072-4079
Published online Aug 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i30.4072
Published online Aug 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i30.4072
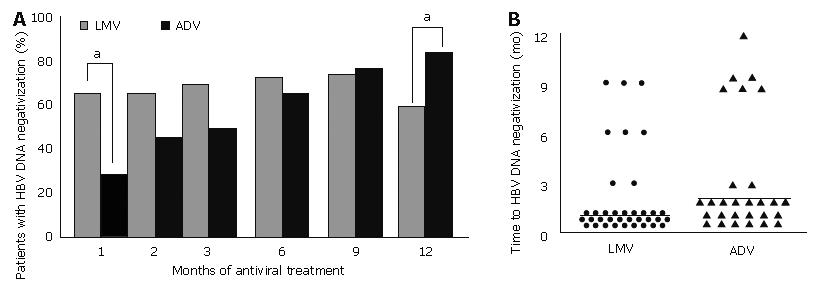
Figure 5 A: Percentage of patients with undectable HBV DNA (by hybridization assay) at months 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 12 after treatment with lamivudine (gray bars) and after switching to adefovir (black bars).
aP < 0.05 vs ADV; B: Time to HBV DNA loss during 12 mo of lamivudine (left) and adefovir (right) treatment. HBV DNA became negative in 36 patients with lamivudine and in 28 patients with adefovir. Note that HBV DNA negativization took about 1 mo longer with adefovir (median 2 mo) compared to lamivudine (median 1 mo; P < 0.05). Times to HBV DNA negativization (by hybridization assay) after lamivudine or adefovir treatment in each patient is represented as ● and ▲, respectively. Horizontal bars (—) represent median time to HBV DNA negativization. LMV: lamivudine; ADV: adefovir dipivoxil.
- Citation: Seo YS, Kim JH, Yeon JE, Park JJ, Kim JS, Byun KS, Bak YT, Lee CH. Antiviral efficacy of adefovir dipivoxil versus lamivudine in patients with chronic hepatitis B sequentially treated with lamivudine and adefovir due to lamivudine resistance. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(30): 4072-4079
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i30/4072.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i30.4072