Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2007; 13(29): 3939-3947
Published online Aug 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i29.3939
Published online Aug 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i29.3939
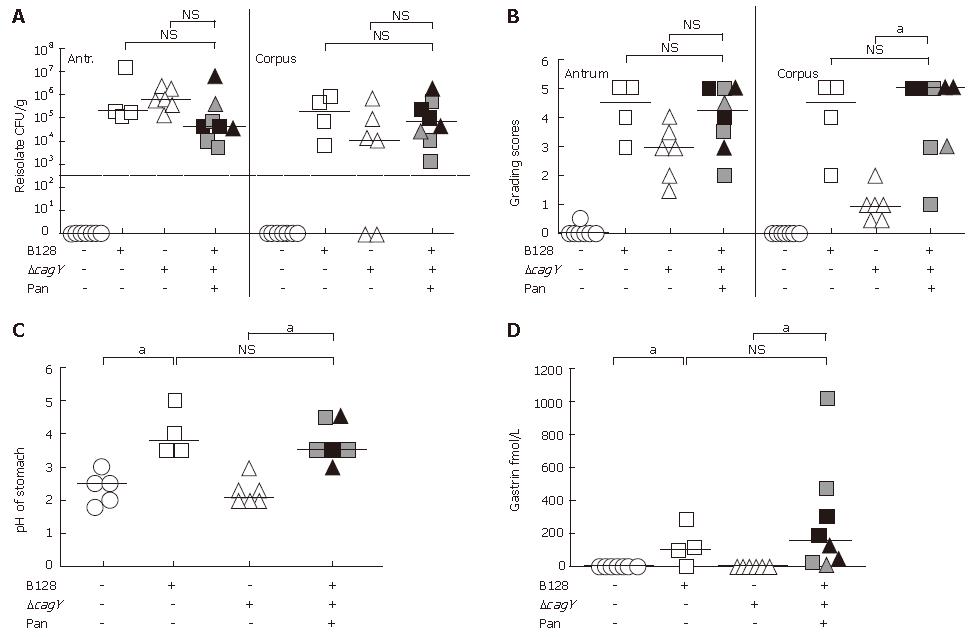
Figure 2 Mongolian gerbils orally challenged with H pylori for seven months.
A: Colonization density; B: histological grading of antral and corpus mucosa; C: Stomach pH; D: Plasma levels of gastrin. Infected animals that developed transmural inflammation (filled grey symbols) and chronic pancreatitis (filled black symbols) [Pan.] showed a severe antral and corpus gastritis, increased pH, and increased plasma gastrin level. The Pan-group represents animals of both infected groups (aP < 0.05).
-
Citation: Rieder G, Karnholz A, Stoeckelhuber M, Merchant JL, Haas R.
H pylori infection causes chronic pancreatitis in Mongolian gerbils. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(29): 3939-3947 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i29/3939.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i29.3939