Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2007; 13(26): 3605-3609
Published online Jul 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i26.3605
Published online Jul 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i26.3605
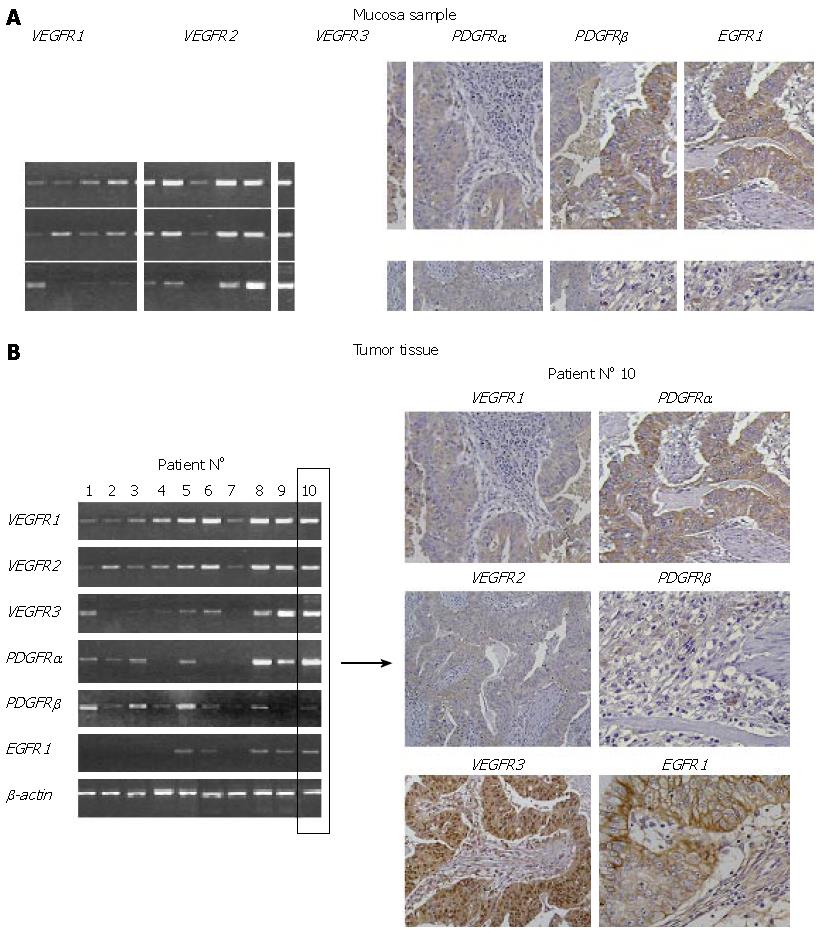
Figure 1 A: The IHC staining of healthy gastric mucosa for VEGFR1-3, PDGFR-α/β and EGFR1.
While healthy gastric mucosa revealed a significant EGFR1 and an intermediate VEGFR2 expression in gastric epithelial cells, all other RTKs exhibited only faint to absent expression levels; B: The exemplary transcription profile of 10 gastric cancers and an immunohistochemical analyses of an adenocarcinoma specimen originating from one patient. While VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3 and PDGFRα revealed a predominantly cytoplasmatic staining accompanied by an additional nuclear staining for VEGFR3, EGFR1 was almost exclusively restricted to the membrane of tumor cells. Stromal cells revealed expression of PDGFRα and PDGFRβ.
- Citation: Drescher D, Moehler M, Gockel I, Frerichs K, Müller A, Dünschede F, Borschitz T, Biesterfeld S, Holtmann M, Wehler T, Teufel A, Herzer K, Fischer T, Berger MR, Junginger T, Galle PR, Schimanski CC. Coexpression of receptor-tyrosine-kinases in gastric adenocarcinoma-a rationale for a molecular targeting strategy? World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(26): 3605-3609
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i26/3605.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i26.3605