Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2007; 13(26): 3598-3604
Published online Jul 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i26.3598
Published online Jul 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i26.3598
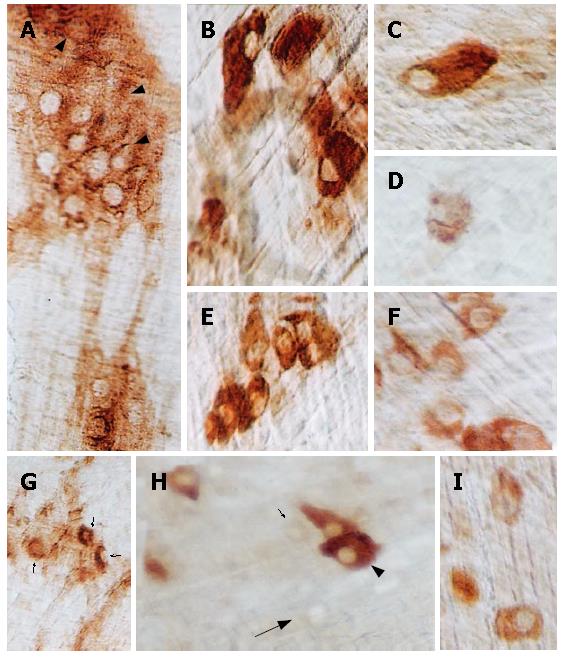
Figure 3 Myenteric plexus of the esophagus from N (A-C, E) and D (D, F-I) rats stained with the AChE technique.
Most N neurons react intensely (A, arrowheads, and B, C, E) while only a few neurons in D are strongly reactive (G, small arrows, and D, F, I). Furthermore, a wide range of staining intensity was observed in some D ganglia, from very intense (H, arrowhead) to poor (H, small arrow). Non-reactive neurons (“shadows”) were also observed in this group (H, large arrow). (A-F, H and I: x 340; G: x 120).
- Citation: Liberti EA, Fontes RB, Fuggi VM, Maifrino LB, Souza RR. Effects of combined pre- and post-natal protein deprivation on the myenteric plexus of the esophagus of weanling rats: A histochemical, quantitative and ultrastructural study. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(26): 3598-3604
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i26/3598.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i26.3598