Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2007; 13(26): 3540-3553
Published online Jul 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i26.3540
Published online Jul 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i26.3540
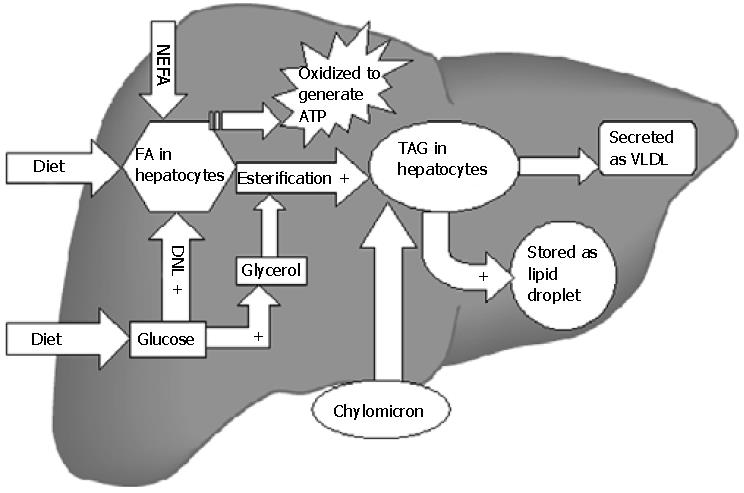
Figure 1 Lipid metabolism in liver.
All steps indicated by + are stimulated by insulin. Insulin suppresses the secretion of VLDL and the β-oxidation of fatty acids. Thus hyperinsulinemia in the setting of insulin resistance favors TAG accumulation in liver. TAG: triglycerides; VLDL: very low density lipoprotein; FA: fatty acid; NEFA: nonesterified fatty acids; DNL: de novo lipogenesis; ATP: adenosine triphosphate.
- Citation: Qureshi K, Abrams GA. Metabolic liver disease of obesity and role of adipose tissue in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(26): 3540-3553
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i26/3540.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i26.3540