Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2007; 13(22): 3071-3079
Published online Jun 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i22.3071
Published online Jun 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i22.3071
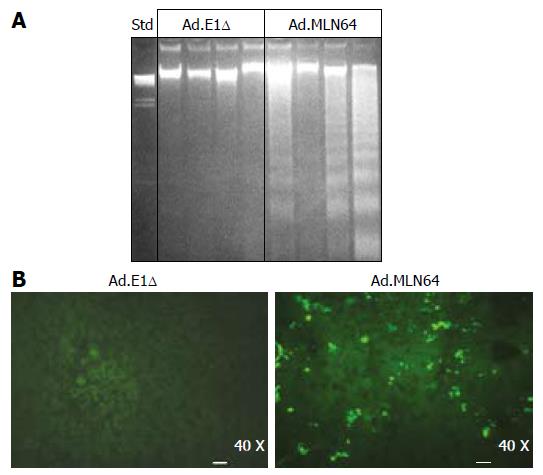
Figure 3 Effect of recombinant MLN64 adenovirus infection on liver apoptosis in mice.
DNA fragmentation analysis and TUNEL assay were performed in murine livers 24 h after infection with Ad.E1Δ or Ad.MLN64 as biochemical markers of apoptosis. A: DNA fragmentation analysis of liver tissue by DNA agarose gel electrophoresis. DNA λ/Hind III was used as the standard (Std); B: TUNEL assay. Substantially more apoptotic cells were detected in liver sections from Ad.MLN64-infected mice than in those from Ad.E1Δ-infected mice. Analysis were performed in four mice in each experimental group. Results are representative of three independent experiments.
- Citation: Tichauer JE, Morales MG, Amigo L, Galdames L, Klein A, Quiñones V, Ferrada C, R AA, Rio MC, Miquel JF, Rigotti A, Zanlungo S. Overexpression of the cholesterol-binding protein MLN64 induces liver damage in the mouse. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(22): 3071-3079
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i22/3071.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i22.3071