Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2007; 13(22): 3071-3079
Published online Jun 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i22.3071
Published online Jun 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i22.3071
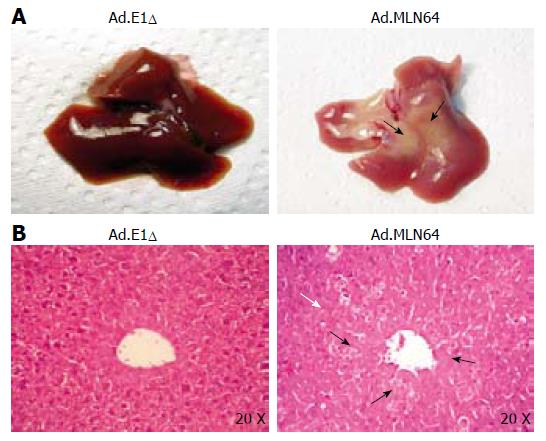
Figure 2 Effect of recombinant MLN64 adenovirus infection on liver morphology and histology in mice.
A: Gross morphology of murine livers 24 h after infection with Ad.E1Δ or Ad.MLN64. Arrows indicate yellowish-white zones with liver necrosis in Ad.MLN64-infected mice; B: Liver sections from (A) were prepared for histology and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Small arrows indicate necrotic zones, and the white arrow indicates an apoptotic zone. Analysis were performed in four mice in each experimental group. Results are representative of three independent experiments.
- Citation: Tichauer JE, Morales MG, Amigo L, Galdames L, Klein A, Quiñones V, Ferrada C, R AA, Rio MC, Miquel JF, Rigotti A, Zanlungo S. Overexpression of the cholesterol-binding protein MLN64 induces liver damage in the mouse. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(22): 3071-3079
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i22/3071.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i22.3071