Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2007; 13(22): 3047-3055
Published online Jun 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i22.3047
Published online Jun 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i22.3047
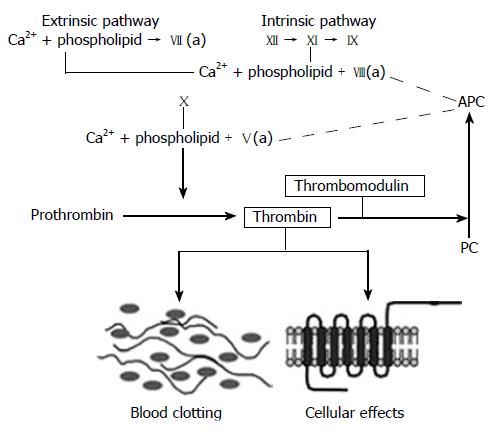
Figure 2 The coagulation cascade.
Simplified diagram of the coagulation “cascade” with the intrinsic, extrinsic, and common pathways. Note how thrombomodulin, located on the luminal surface of endothelial cells, forms a complex with thrombin, which is converted from a pro-coagulant to an anticoagulant and how activated protein C (APC) limits thrombin generation by feed-back into the intrinsic and common coagulation pathways. See text for further details.
- Citation: Wang J, Boerma M, Fu Q, Hauer-Jensen M. Significance of endothelial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of early and delayed radiation enteropathy. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(22): 3047-3055
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i22/3047.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i22.3047