Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2007; 13(21): 2923-2931
Published online Jun 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i21.2923
Published online Jun 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i21.2923
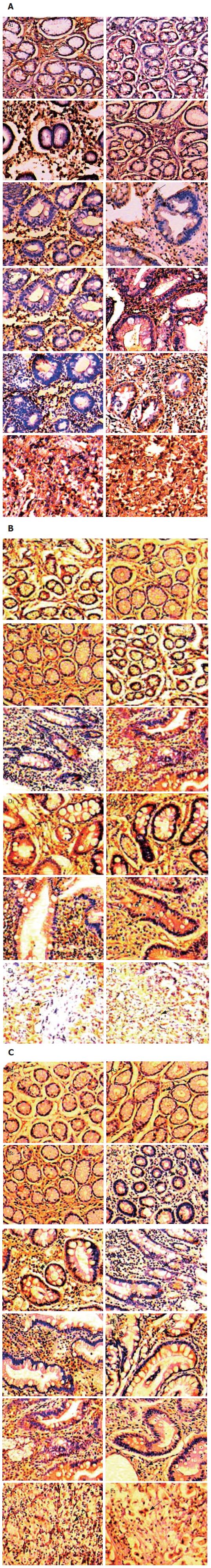
Figure 5 Representatives of immunohistochemistry staining for IFN-γ and IL-4 in gastric biopsies of CagA+ H.
pylori (A), CagA- H pylori (B) and those without H pylori infected patients(C) with normal gastric mucosa or with different gastric pathologies (DAB, ×200, Arrowhead shows the representative positive cells, which are stained brown). A1, B1, C1, D1, E1 and F1 represent IFN-γ expression in normal mucosa (NM), chronic gastritis (CG), gastric atrophy (GA), intestinal metaplasia (IM) and gastric cancer (GC), respectively, and A2, B2, C2, D2, E2 and F2 represent IL-4 expression in NM, CG,GA,IM, DP AND GC, respectively. A: The rates of IFN-γ+ cells are great in the CG, GA, and IM groups relative to the DP and GC groups. Additionally, the rates of IL-4+ cells are less in the NC and CG groups, but increased along the progression; B: The rates of IFN-γ+ cells and IL-4+ cells were constant in all the groups, and IFN-γ expression with “++” was dominant, while IL-4 expression with “+” was in the majority of all the groups; C: The rates of IFN-γ+ cells and IL-4+ cells were constant in all the groups, and IFN-γ expression with “++” was dominant, while IL-4 expression with “+” was in the majority of all the groups.
-
Citation: Wang SK, Zhu HF, He BS, Zhang ZY, Chen ZT, Wang ZZ, Wu GL. CagA+
H pylori infection is associated with polarization of T helper cell immune responses in gastric carcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(21): 2923-2931 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i21/2923.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i21.2923