Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2007; 13(21): 2923-2931
Published online Jun 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i21.2923
Published online Jun 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i21.2923
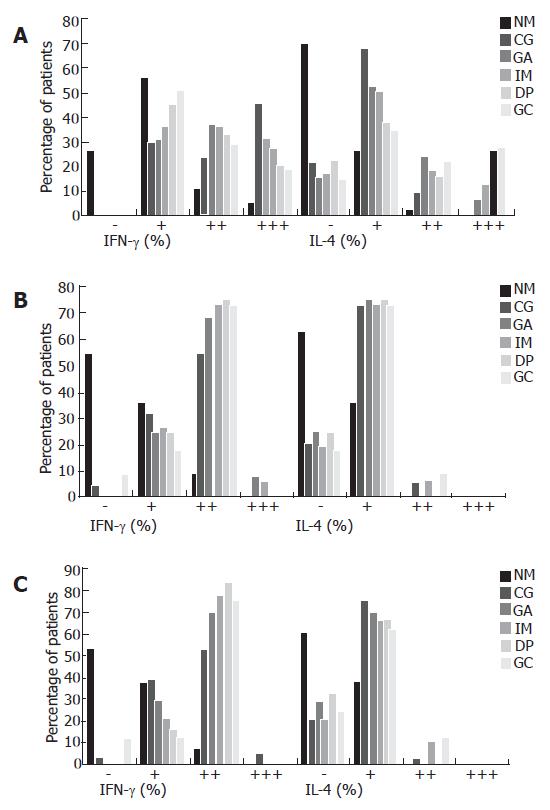
Figure 4 Local immunity responses in patients with CagA+ (A) , CagA- H pylori (B) infection and those without H pylori infection (C) as determined by immunohistochemistry.
Numbers of IFN-γ and IL-4 positive cells from 200 polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) and mononuclear cells (MNCs) were counted from five randomly chosen fields and averaged. The positive rate was used to grade the expression levels: negative: 0%; +: 1%-25%; ++ 26%-50%; +++, 51%-100%. A: IFN-γ expression with “+++” predominates in chronic gastritis (CG), while IFN-γ expression with “+” becomes the majority when the disease develops to gastric cancer (GC). On the contrary, IL-4 expression with “+” decreases gradually when the disease develops from CG to GC, but the rate of IL-4 expression with “+++” increases gradually following the progression; B: Following the progression of gastric lesions, there was no difference of IFN-γ and IL-4 expression in that the former was always with “++”, while the latter was always with “+” in all the groups; C: Following the progression of gastric lesions, IFN-γ expression with “++” were at all dominant, while IL-4 expression with “+” was in the main in all the groups.
-
Citation: Wang SK, Zhu HF, He BS, Zhang ZY, Chen ZT, Wang ZZ, Wu GL. CagA+
H pylori infection is associated with polarization of T helper cell immune responses in gastric carcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(21): 2923-2931 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i21/2923.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i21.2923