Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2007; 13(20): 2811-2818
Published online May 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i20.2811
Published online May 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i20.2811
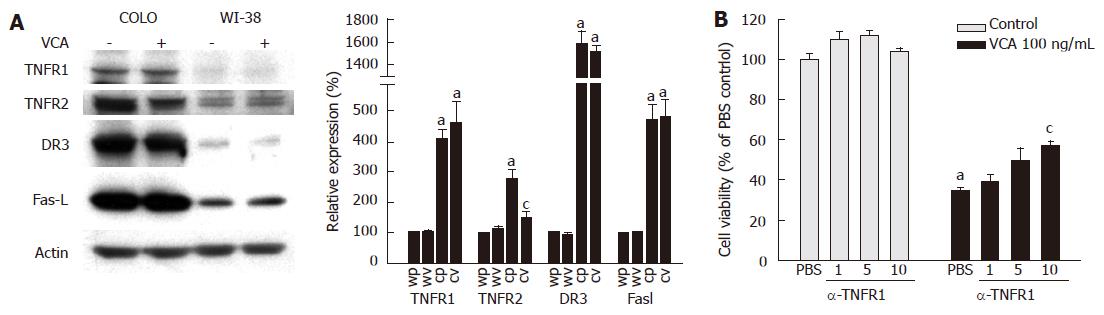
Figure 5 Inhibition of VCA-induced cytotoxicity of COLO cells by antagonizing anti-TNFR1 antibody (A) COLO and WI-38 cells were treated without (-) or with (+) VCA (100 ng/mL) for 12 h, cell lysates were prepared, and western blots were performed using specific antibodies.
Immunoreactive bands were visualized by chemiluminescence. Representative western blot is shown (left panel). Each band was quantified and normalized against the density of the internal control (®-actin). Normalized values were used to calculate the relative expression as a percentage of PBS-treated WI-38 cells. WP: WI-38 cells treated with PBS, WV: WI-38 cells treated with VCA, CP: COLO cells treated with PBS, CV: COLO cells treated with VCA. Values are mean±SE of three independent experiments (right panel). aP < 0.05 vs WP. cP < 0.05 vs CP. (B) COLO cells were treated without (Control) or with VCA (100 ng/mL) in the absence (PBS) or presence of the indicated amounts of antagonizing TNFR1 antibody (®-TNFR1) for 12 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay. Values are mean ± SE (n = 4). aP < 0.05 vs the PBS-treated control group. cP < 0.05 vs the PBS/VCA-treated group.
- Citation: Khil LY, Kim W, Lyu S, Park WB, Yoon JW, Jun HS. Mechanisms involved in Korean mistletoe lectin-induced apoptosis of cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(20): 2811-2818
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i20/2811.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i20.2811