Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2007; 13(2): 192-218
Published online Jan 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.192
Published online Jan 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.192
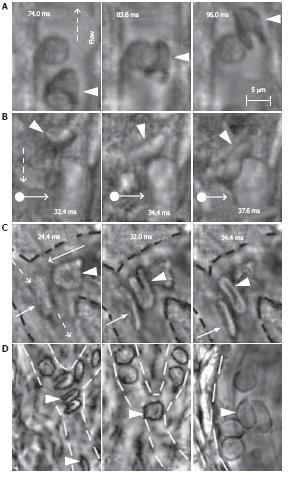
Figure 12 High-resolution, high-speed monitoring of cells in blood flow.
RBCs are indicated by conventional arrows and triangle; rolling WBCs by arrows originating from filled circles; and direction of flow by dashed lines. A-C: behavior of normal RBCs and WBCs in flow (1250-2500 fps; 40 ×); D: The shapes of normal (left) and diamide-treated (middle) RBCs in single-file flow of small venula (diameter ~10 μm), and (right) adhesion of diamide-treated RBCs to wall of the relatively large venula (diameter -40 μm).
-
Citation: Galanzha EI, Tuchin VV, Zharov VP. Advances in small animal mesentery models for
in vivo flow cytometry, dynamic microscopy, and drug screening. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(2): 192-218 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i2/192.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.192