Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2007; 13(2): 175-191
Published online Jan 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.175
Published online Jan 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.175
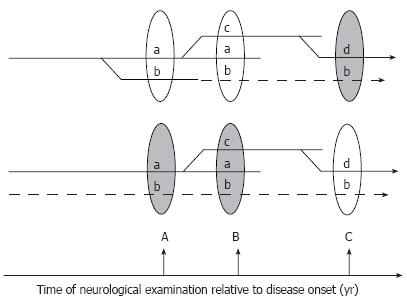
Figure 5 Hypothetical branching (top) and multi-trigger (bottom) pathogenesis of DPN.
In the first scenario (top) all manifestations of the disease result from the unique branching pathogenic process, and symptom “b” discovered at the time of neurological exam B is not corrected by treatment because it has already progressed to an irreversible stage (dashed lines). Earlier diagnosis and institution of treatment (at time A) may critically change the outcome of therapy in this scenario. Alternatively (lower scenario), several independent factors may trigger and maintain the progression of DPN. In this case the therapy may fail to treat symptoms not because they are irreversible, but because the correct cause of the pathology is not identified and is not treated (dashed lines).
- Citation: Dobretsov M, Romanovsky D, Stimers JR. Early diabetic neuropathy: Triggers and mechanisms. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(2): 175-191
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i2/175.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.175