Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2007; 13(19): 2707-2716
Published online May 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i19.2707
Published online May 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i19.2707
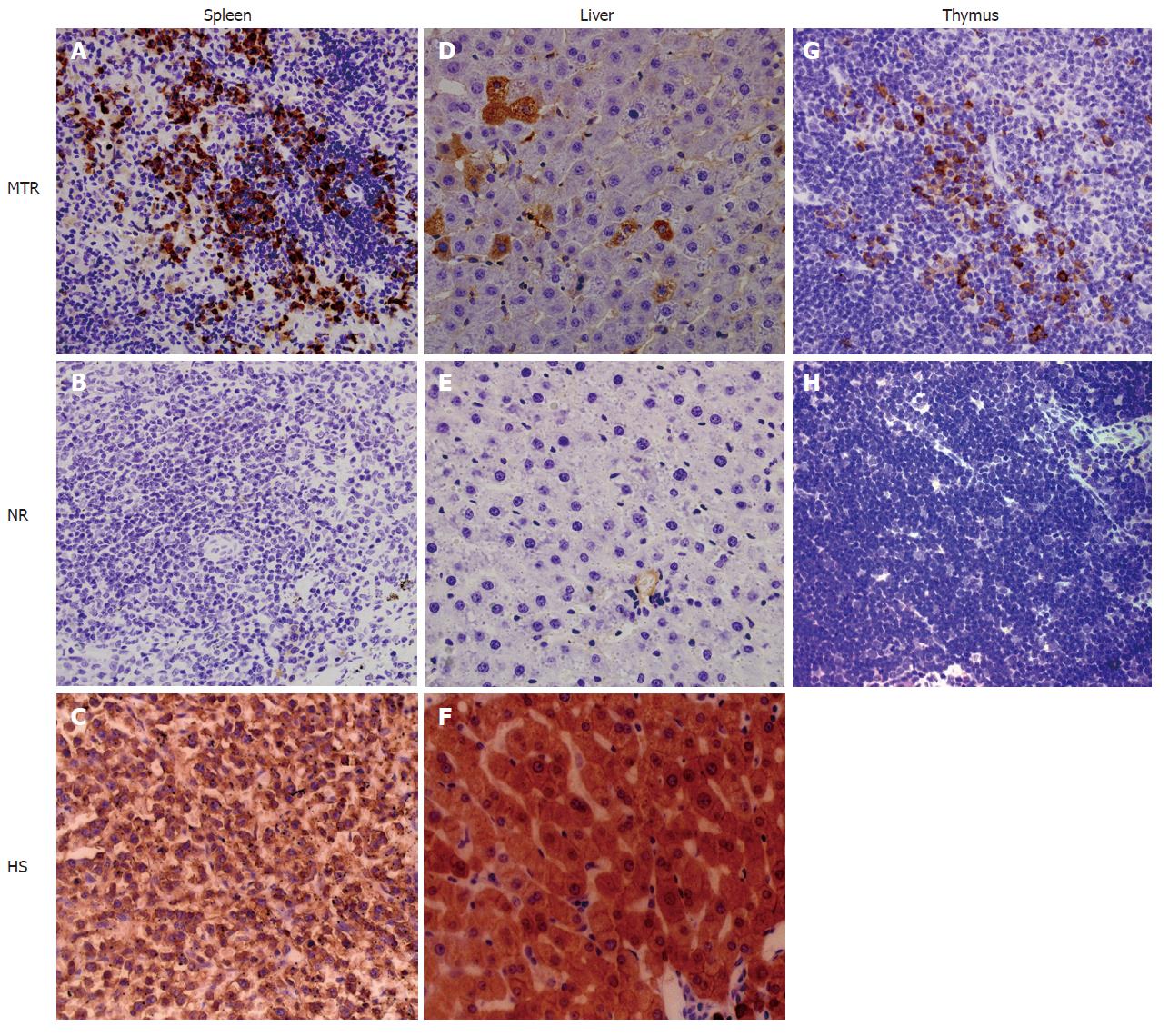
Figure 4 Evidences for site-specific human cell differentiation in the xenogeneic system.
Transplanted UCB-derived human cells underwent site-specific differentiation in various tissues [i.e. liver, spleen and thymus] of MNC-transplanted rats, as confirmed by using human-specific differentiation markers (such as CK18 and CD45). Brown staining shows CD45-positive human cells in the spleen (A and C) and thymus (G) of MNC-transplanted rats (MTR) and human samples (HS), whereas no positive human cells are found in the spleen (B) and thymus (H) of normal control rats (NR). Livers (D and F) from MTR and HS are uniformly positive for CK18, while liver (E) from NR is negative for CK18.
-
Citation: Sun Y, Xiao D, Pan XH, Zhang RS, Cui GH, Chen XG. Generation of human/rat xenograft animal model for the study of human donor stem cell behaviors
in vivo . World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(19): 2707-2716 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i19/2707.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i19.2707