Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2007; 13(17): 2416-2426
Published online May 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i17.2416
Published online May 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i17.2416
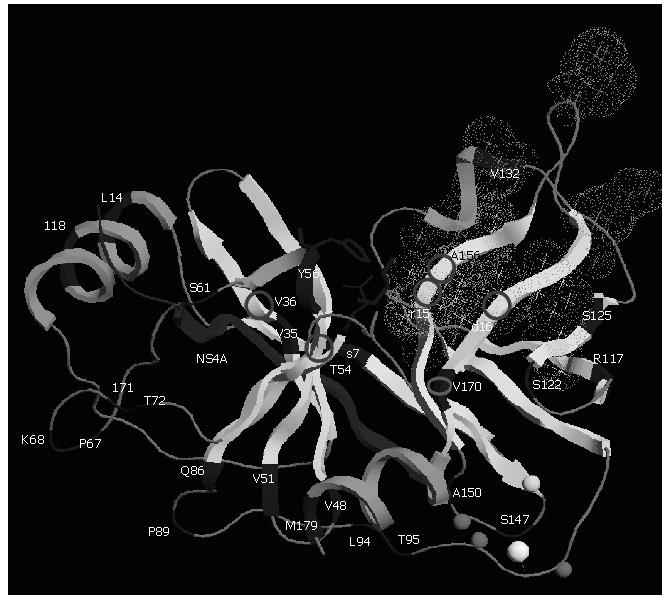
Figure 4 Three-dimensional structure of NS3 protease (PDB accession code 1NS3).
Polymorphism and main residues implicated in resistance are shown. The protease is shown based on its secondary structure in light grey. Main polymorphic residues are shown in dark grey. The side chains of the residues forming the catalytic triad (H57, D81, and S139) are displayed in dark grey ball-and-stick representation. The NS4A cofactor is shown in dark grey and Zinc ion as a white ball. Zn2+ ligands (C97, C99 and C149) and H145 residue are modeled in light grey spheres. Stars correspond to the side chains of the residues forming the S1 to S6 substrate binding pockets (grey dots cloud) of the enzyme. Residues implicated in resistance to protease NS3 inhibitors are shown with circles. This figure was prepared using the RasTop programme version 2.0.3-VF.
- Citation: Le Guillou-Guillemette H, Vallet S, Gaudy-Graffin C, Payan C, Pivert A, Goudeau A, Lunel-Fabiani F. Genetic diversity of the hepatitis C virus: Impact and issues in the antiviral therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(17): 2416-2426
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i17/2416.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i17.2416