Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2007; 13(1): 91-103
Published online Jan 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i1.91
Published online Jan 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i1.91
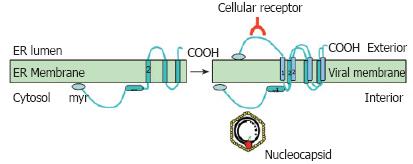
Figure 5 Dual topology of the viral surface protein L.
The L protein is inserted into the ER membrane during synthesis with transmembrane domain 2 being inserted into the membrane. Half of the proteins then change their topology and insert the transmembrane domain 1 into the ER membrane. After this change and formation of the virus, L can exert its two basic functions; interaction with the nucleocapsid on the cytosolic preS domain and interaction with the host cell receptor on the surface of the viral particle.
- Citation: Funk A, Mhamdi M, Will H, Sirma H. Avian hepatitis B viruses: Molecular and cellular biology, phylogenesis, and host tropism. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(1): 91-103
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i1/91.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i1.91