Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2007; 13(1): 48-64
Published online Jan 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i1.48
Published online Jan 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i1.48
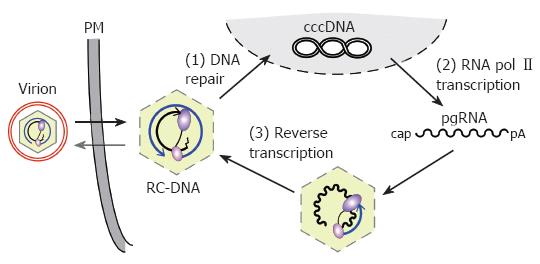
Figure 1 Replication cycle of the hepadnaviral genome.
Enveloped virions infect the cell, releasing RC-DNA containing nucleocapsids into the cytoplasm. RC-DNA is transported to the nucleus, and repaired to form cccDNA (1). Transcription of cccDNA by RNA polymerase II (2) produces, amongst other transcripts (not shown), pgRNA. pgRNA is encapsidated, together with P protein, and reverse transcribed inside the nucleocapsid (3). (+)-DNA synthesis from the (-)-DNA template generates new RC-DNA. New cycles lead to intracellular cccDNA amplification; alternatively, the RC-DNA containing nucleocapsids are enveloped and released as virions. PM, plasma membrane.
- Citation: Beck J, Nassal M. Hepatitis B virus replication. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(1): 48-64
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i1/48.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i1.48