Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2006; 12(6): 885-895
Published online Feb 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.885
Published online Feb 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.885
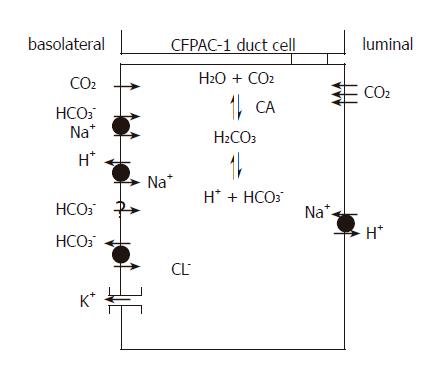
Figure 10 H+ and HCO3– transport mechanisms in CFPAC-1 human pancreatic duct cells.
The basolateral membrane expresses Na+/HCO3– co-transporters, Na+/H+ exchangers and Cl–/HCO3– exchangers plus an unidentified Na+-independent HCO3– entry pathway. These transporters facilitate the rapid flux of HCO3– ions into the cell. K+ channels are also likely to be expressed on the basolateral membrane because altering extracellular K+ concentration affects HCO3– influx. The apical membrane expresses Na+/H+ exchangers, but not CFTR and Cl–/HCO3– exchangers found in normal pancreatic duct cells. The apical membrane is an effective barrier to HCO3– influx from the lumen, but is freely permeable to CO2. CA: Carbonic anhydrase.
- Citation: Jr ZR, Fearn A, Hegyi P, Boros I, Gray MA, Argent BE. Characterization of H+ and HCO3- transporters in CFPAC-1 human pancreatic duct cells. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(6): 885-895
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i6/885.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.885