Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2006; 12(6): 885-895
Published online Feb 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.885
Published online Feb 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.885
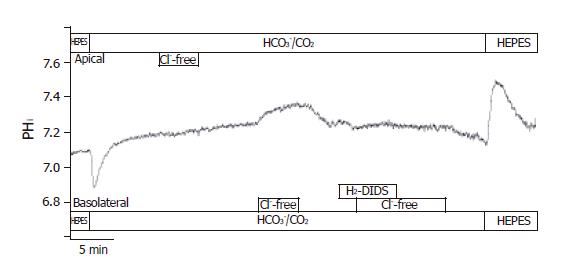
Figure 7 Localization of Cl–/HCO3– exchangers in CFPAC-1 cells.
The figure shows representative pHi traces (n = 6). The localization of Cl–/HCO3– exchangers was performed by measuring the effect of changes in Cl– gradient across the luminal or basolateral membranes on pHi. In the presence of HCO3–, the removal of Cl– from the apical membrane did not result in changes of pHi. The removal of Cl– from the basolateral membrane caused a ∆pHi of 0.08 ± 0.01 and a J(B) of 4.37 ± 0.46 mmol/L B/min. Furthermore, the basolateral administration of 250 µmol/L H2-DIDS completely blocked pHi changes caused by the withdrawal of Cl–.
- Citation: Jr ZR, Fearn A, Hegyi P, Boros I, Gray MA, Argent BE. Characterization of H+ and HCO3- transporters in CFPAC-1 human pancreatic duct cells. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(6): 885-895
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i6/885.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.885