Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2006; 12(46): 7497-7502
Published online Dec 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7497
Published online Dec 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7497
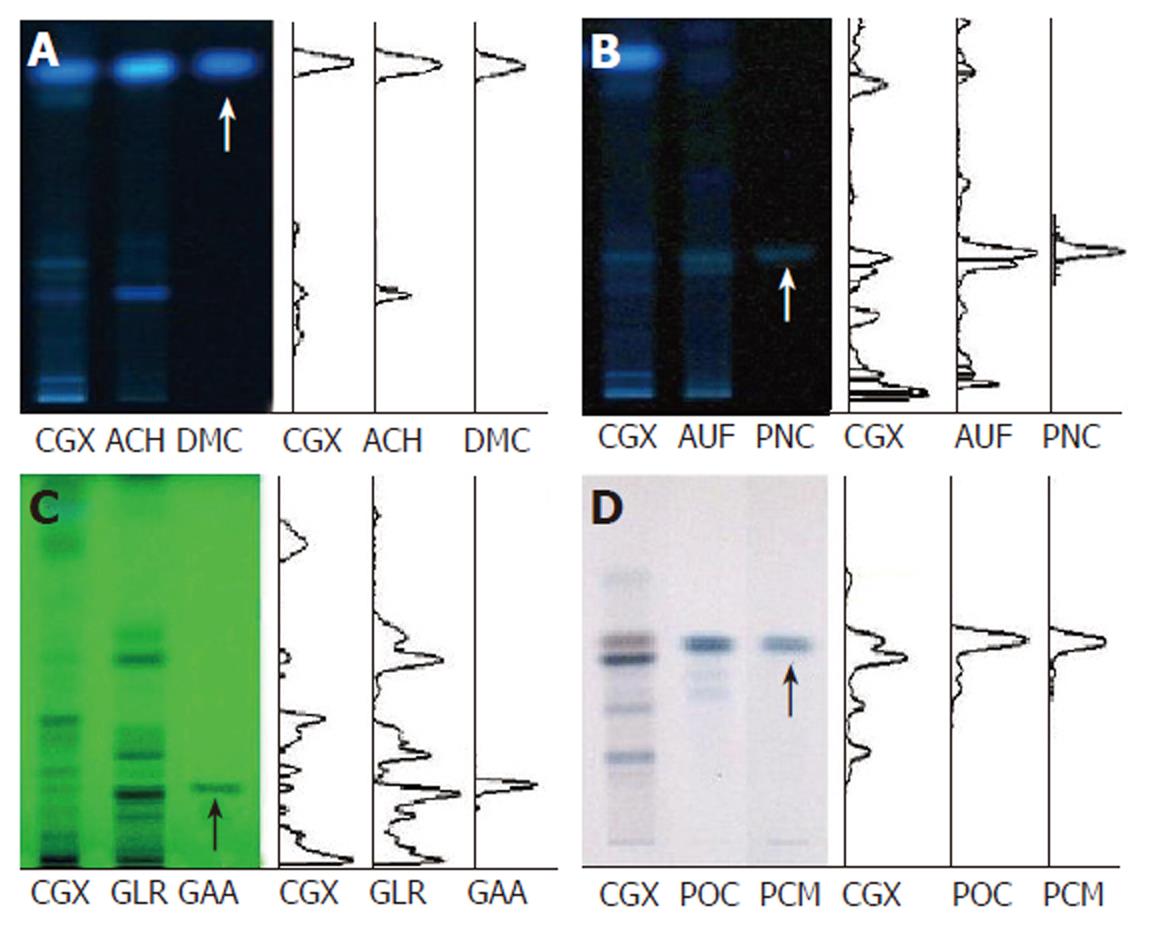
Figure 1 High-performance thin layer chromatography method-based fingerprint for Chunggan extract.
HPTLC analysis was performed to characterize CGX and its three major components (extracts from Artemisia capillaris Herba, Aurantii Fructus, Glycyrrhizae Radix and Poria cocos) with reference components, 6,7-dimethoxycoumarin, Poncirin, Glycyrrhizic acid ammonium salt and Pachyman (indicated by arrows). A: 2 μL of CGX (200 mg/mL) and 1 μL of the extract from Artemisia capillaris Herba (50 mg/mL) were subjected to HPTLC with 1 μL of 6,7-dimethoxycoumarin (0.1 mg/mL), then visualized under UV radiation at 366 nm; B: 2 μL of CGX (200 mg/mL) and 1 μL of the extract from Aurantii Fructus (50 mg/mL) were subjected to HPTLC with 1 μL of Poncirin (5 mg/mL), then visualized under UV radiation at 366 nm; C: 4 μL of CGX (200 mg/mL) and 4 μL of the extract from Glycyrrhizae Radix (50 mg/mL) were subjected to HPTLC with 4 μL of Glycyrrhizic acid ammonium salt (1 mg/mL), then visualized under UV radiation at 254 nm; D: 2 μL of CGX (40 mg/mL) and 1 μL of the extract from Poria cocos (10 mg/mL) were subjected to HPTLC with 10 μL of Pachyman (100 mg/mL), then visualized under white light after derivatization.
- Citation: Choi WJ, Shin JW, Son JY, Seo DS, Park HS, Han SH, Sung HJ, Cho JH, Cho CK, Yoo HS, Lee YW, Son CG. Toxicological study of the hepatotherapeutic herbal formula, Chunggan extract, in beagle dogs. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(46): 7497-7502
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i46/7497.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7497