Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2006; 12(46): 7488-7496
Published online Dec 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7488
Published online Dec 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7488
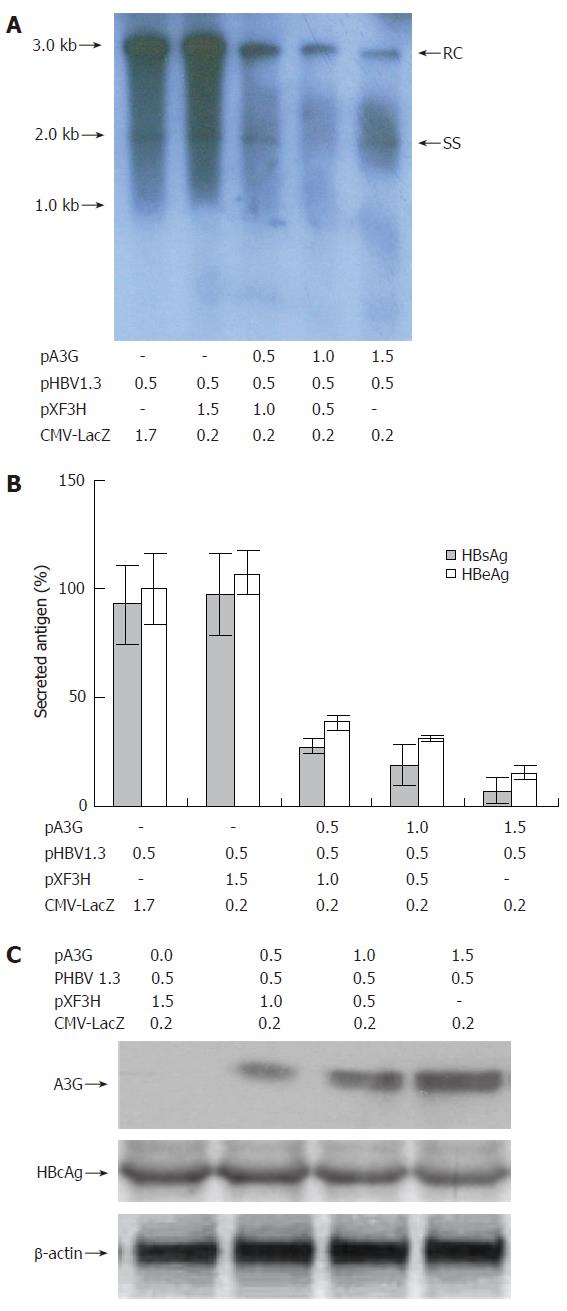
Figure 2 Effect of APOBEC3G on HBV replication in co-transfected HepG2 cells.
(A) Human hepatoma HepG2 cells were transiently co-transfected with pHBV1.3 and various amounts of a CMV-driven expression vector encoding A3G or with empty vector pXF3H and pCMV-LacZ using Lipofectamine 2000 reagents. The cells were harvested 3 d after transfection. HBV core-associated viral DNA was prepared from nuclease-treated cytoplasmic lysates. Viral replicative DNA intermediates were analyzed by Southern blotting using a Dig-labeled full-length HBV DNA probe. (B) HBsAg and HBeAg levels were determined in the media of co-transfected HepG2 cells by ELISA, normalized to the activity of co-tansfected β-galactosidase in the cell lysates. The mean ± SE of six independent experiments is shown (error bar indicates standard error). (C) Western blot analysis of cytoplasmic extracts from HepG2 cells co-transfected with the indicated plasmids. Numbers at the end or top of the lines indicate the amount of transfected plasmid DNA in micrograms. HBV: hepatitis B virus; pA3G: APOBEC3G expression plasmids; RC: relaxed circular DNA; SS: single-stranded DNA; HBcAg: hepatitis B virus core antigen; HBsAg: hepatitis B virus surface antigen; HBeAg: hepatitis B virus e antigen.
- Citation: Lei YC, Tian YJ, Ding HH, Wang BJ, Yang Y, Hao YH, Zhao XP, Lu MJ, Gong FL, Yang DL. N-terminal and C-terminal cytosine deaminase domain of APOBEC3G inhibit hepatitis B virus replication. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(46): 7488-7496
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i46/7488.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7488