Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2006; 12(46): 7451-7459
Published online Dec 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7451
Published online Dec 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7451
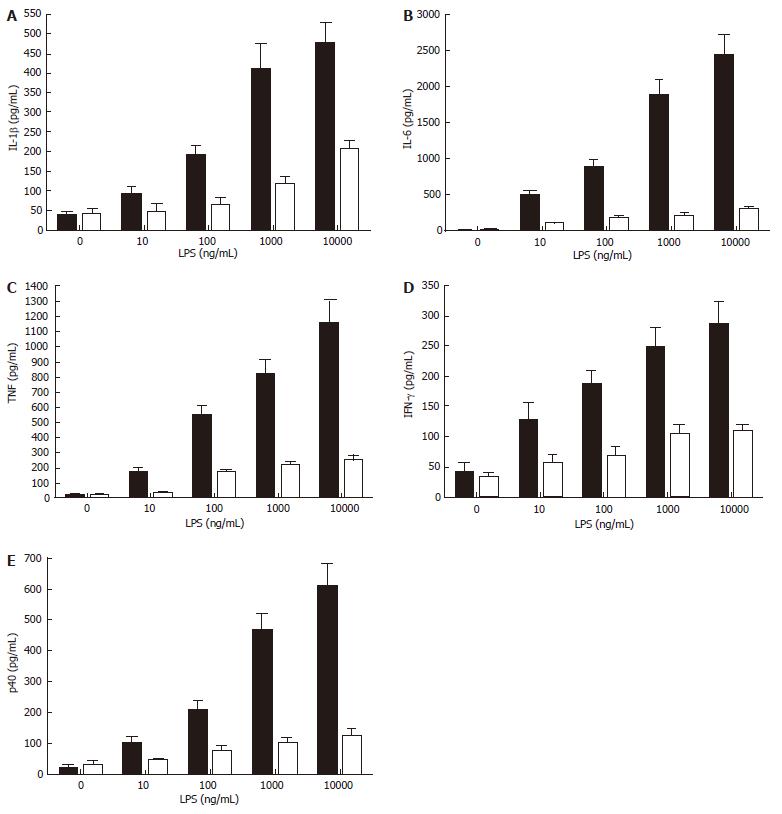
Figure 4 Nicotine inhibits the release of multiple cytokines (TNF, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-6, and the common IL-12/IL-23 subunit, p40) under the control of the NF-κB pathway.
Cells were pre-treated with nicotine (100 ng/mL) for 2 h then stimulated with purified LPS (0 to 1 x 104 ng/mL) for 24 h. Cell-free supernatants were harvested by centrifugation and levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines were determined by ELISA. Data represents the mean (SD) of triplicate experiments.
- Citation: Scott DA, Martin M. Exploitation of the nicotinic anti-inflammatory pathway for the treatment of epithelial inflammatory diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(46): 7451-7459
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i46/7451.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7451