Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2006; 12(46): 7397-7404
Published online Dec 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7397
Published online Dec 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7397
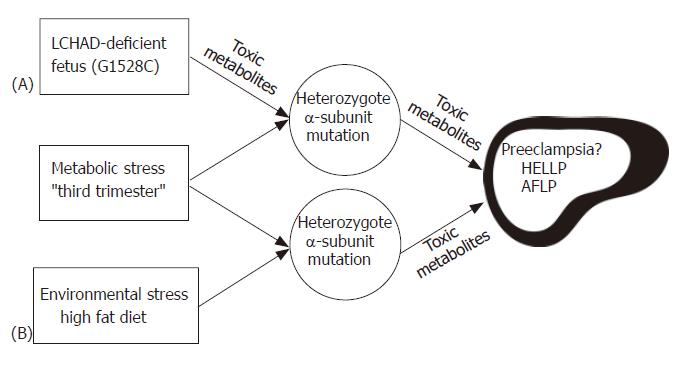
Figure 4 Hypothesis illustrating the possible role of fetal and maternal MTP mutations in developing AFLP.
Carrying an LCHAD deficient fetus (A) is the major determining factor in the development of maternal illness. Hepatotoxic metabolites produced by the fetus and/or placenta may cause liver disease in the obligate heterozygous mother when combined with the metabolic stress of the third trimester. Environmental stress (B) may lead to the further accumulation of toxic metabolites in the genetically susceptible mother causing maternal liver disease.
- Citation: Ibdah JA. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy: An update on pathogenesis and clinical implications. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(46): 7397-7404
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i46/7397.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7397