Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2006; 12(44): 7118-7125
Published online Nov 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i44.7118
Published online Nov 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i44.7118
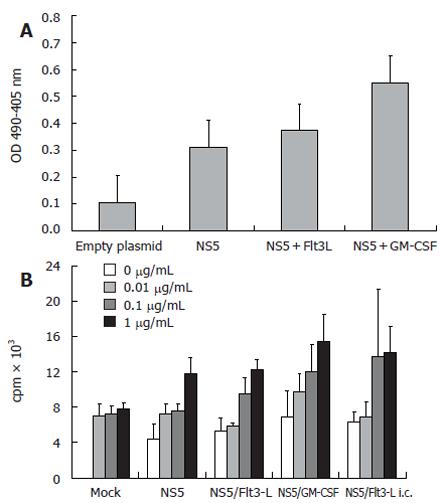
Figure 3 A: Anti-HCV NS5 ELISA showing mean levels of specific antibodies after genetic immunization with HCV-NS5-expressing plasmid.
Controls included wells coated with BSA and sera derived from mock-immunized mice. Each group comprised 10 BALB/c mice and mice sera were pooled before the assay. ELISA plates were coated with HCV-NS5-4, therefore, antibody levels may be underestimated; B: T-cell proliferation assay (n = 10 mice/group) with different amounts of stimulating recombinant HCV NS5-4 protein (0.01-1 µg/mL). An increase of thymidine incorporation was seen after stimulation with 0.1 and 1 µg/mL recombinant protein. However, levels of T-cell proliferation after co-immunization with Flt3-L were only slightly higher than in NS5-immunized mice. Note that stimulation with a non-relevant protein (HBsAg) induced only background activity, demonstrating the antigen specificity (data not shown).
- Citation: Encke J, Bernardin J, Geib J, Barbakadze G, Bujdoso R, Stremmel W. Genetic vaccination with Flt3-L and GM-CSF as adjuvants: Enhancement of cellular and humoral immune responses that results in protective immunity in a murine model of hepatitis C virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(44): 7118-7125
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i44/7118.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i44.7118