Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2006; 12(42): 6818-6827
Published online Nov 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i42.6818
Published online Nov 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i42.6818
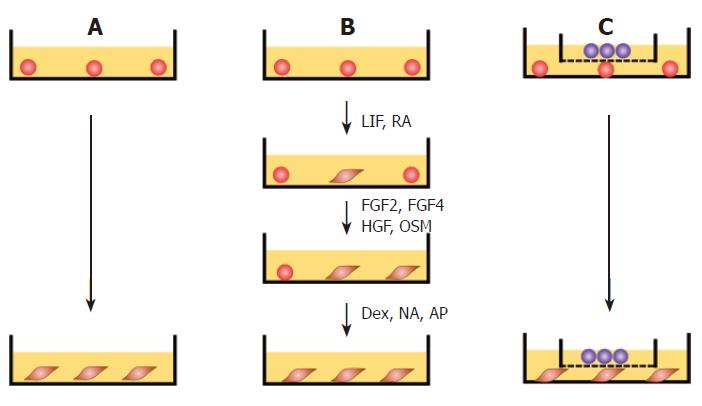
Figure 1 Protocol for differentiation of cES cells.
A: Spontaneous differentiation. Undifferentiated cES cells were cultured in gelatin-coated dishes in DMEM basic medium for 28 d without additional feeders or growth factors; B: GF-induced differentiation. Undifferentiated cES cells were cultured in DMEM basic medium containing LIF (100 units/mL) and RA (10-8 mol/L) for 3 d, followed by a 5-d culture in DMEM basic medium containing FGF2 (10 mg/L), FGF4 (20 mg/L), HGF (25 mg/L), and OSM (10 mg/L). Thereafter, the cells were cultured for 20 d in DMEM basic medium containing 10-7 mol/L dexamethasone (Dex), 0.2 mmol/L, L-ascorbic-2-phosphate (AP), and 10 mmol/L nicotinamide (NA); C: Promoted differentiation by co-culture with MFLCs. Undifferentiated cES cells were plated onto 60-mm dishes and co-cultured with MFLCs in a 35-mm culture insert across a 0.4-μm Millicell CM membrane for 28 d.
- Citation: Saito K, Yoshikawa M, Ouji Y, Moriya K, Nishiofuku M, Ueda S, Hayashi N, Ishizaka S, Fukui H. Promoted differentiation of cynomolgus monkey ES cells into hepatocyte-like cells by co-culture with mouse fetal liver-derived cells. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(42): 6818-6827
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i42/6818.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i42.6818