Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2006; 12(42): 6786-6791
Published online Nov 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i42.6786
Published online Nov 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i42.6786
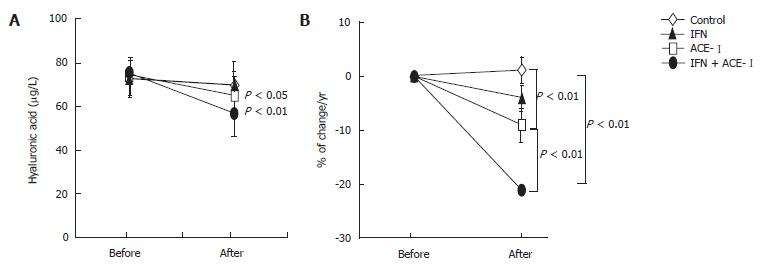
Figure 1 The effects of IFN and ACE-I on the serum hyaluronic acid in the patients with refractory chronic hepatitis C.
A: Hyaluronic acid level before and after the study; B: % of change in the hyaluronic acid level in each group. Control: untreated control group; ACE-I, IFN: ACE-I- and IFN-treated groups, respectively; IFN + ACE-I: combination treated group with ACE-I and IFN. The data represent the mean ± SD.
- Citation: Yoshiji H, Noguchi R, Kojima H, Ikenaka Y, Kitade M, Kaji K, Uemura M, Yamao J, Fujimoto M, Yamazaki M, Toyohara M, Mitoro A, Fukui H. Interferon augments the anti-fibrotic activity of an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor in patients with refractory chronic hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(42): 6786-6791
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i42/6786.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i42.6786