Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2006; 12(4): 526-538
Published online Jan 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i4.526
Published online Jan 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i4.526
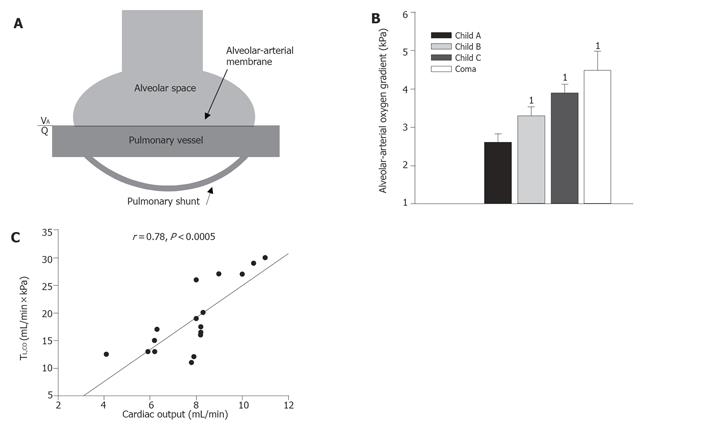
Figure 5 Panel A.
Lung diffusion and blood oxygenation depend on the diffusion properties of the alveolar-arterial membrane, the degree of arterial-venous shunting through pulmonary shunts, and the degree of ventilation-perfusion inequality (VA/Q). Panel B. The alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient increases with the severity of liver disease e.g. graduated according to the Child-Turcotte classification with the highest values in patients with hepatic coma. 1denotes significant difference from Child class A patients (from Ref. [143]). Panel C. In cirrhosis, the diffusing capacity bears a direct relation to the increased cardiac output and to the central blood volume (not shown). Data from Ref. [45].
- Citation: Møller S, Henriksen JH. Cardiopulmonary complications in chronic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(4): 526-538
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i4/526.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i4.526