Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2006; 12(39): 6316-6324
Published online Oct 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i39.6316
Published online Oct 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i39.6316
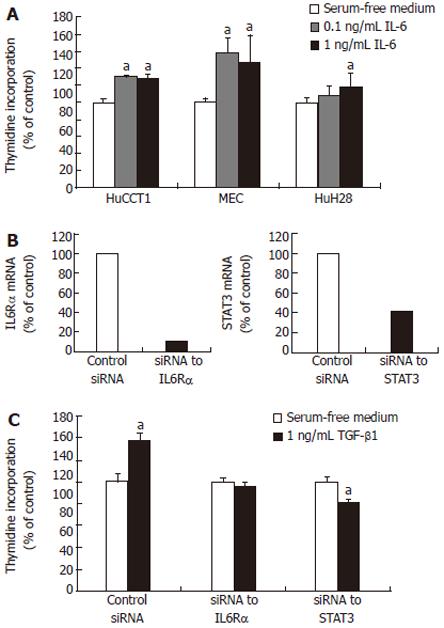
Figure 5 Effects of TGF-β1 on DNA synthesis during inhibition of IL-6 functions.
A: All of the ICC cells demonstrated enhanced DNA synthesis in response to IL-6: aP < 0.05 vs absence of IL-6. We next investigated whether TGF-β1 promoted ICC cell growth during the inhibition of IL-6 functions by small interfering RNA (siRNA); B: RT-PCR was conducted to assess the effects of siRNA in suppressing the mRNA expressions of IL-6Rα and STAT3. IL-6Rα and STAT3 mRNA expression was suppressed by 10.6% and 41.9%, relative to control siRNA; C: The silencing of IL-6Rα and STAT3 mRNA expressions by siRNA in HuCCT1 cells led to a suppression in the TGF-β1-induced DNA synthesis relative to that observed under the control siRNA condition: aP < 0.05 vs absence of rhTGF-β1.
- Citation: Shimizu T, Yokomuro S, Mizuguchi Y, Kawahigashi Y, Arima Y, Taniai N, Mamada Y, Yoshida H, Akimaru K, Tajiri T. Effect of transforming growth factor-β1 on human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell growth. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(39): 6316-6324
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i39/6316.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i39.6316