Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2006; 12(39): 6316-6324
Published online Oct 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i39.6316
Published online Oct 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i39.6316
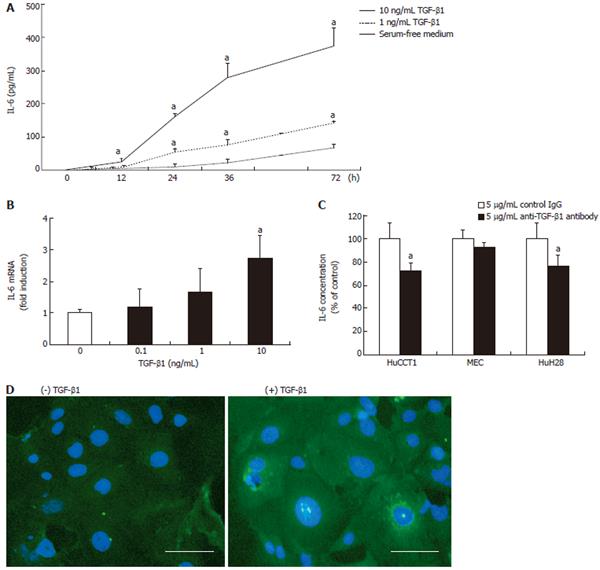
Figure 4 Effect of TGF-β1 on the IL-6 expression of ICC cells.
A: ELISA revealed the secretion of IL-6 by HuCCT1 into the serum-free medium. HuCCT1 also showed a time-dependent increase of IL-6 concentrations in response to 1 and 10 ng/mL TGF-β1 stimulation: aP < 0.05 vs absence of TGF-β1; B: The addition of TGF-β1 to HuCCT1 for 6 h resulted in a dose-dependent increase of IL-6 mRNA expression by RT-PCR: aP < 0.05 vs absence of TGF-β1; C: IL-6 levels in the supernatants were determined by ELISA after incubating ICC cells with 5 ng/mL neutralizing anti-TGF-β1 antibody or nonimmune control IgG for 96 h. The addition of neutralizing anti-TGF-β1 antibody resulted in a decrease of IL-6 production in HuCCT1 and HuH28: aP < 0.05 vs control IgG; D: An immunofluorescence study using HuCCT1 cells demonstrated an increase in IL-6 production in response to TGF-β1. Immunoreactivity with a specific anti-IL6 antibody was weak, with no stimulation of TGF-β1, whereas 10 ng/mL TGF-β1 induced IL-6 expression in the cytoplasm of the HuCCT1 cells. Scale bar = 20 μm.
- Citation: Shimizu T, Yokomuro S, Mizuguchi Y, Kawahigashi Y, Arima Y, Taniai N, Mamada Y, Yoshida H, Akimaru K, Tajiri T. Effect of transforming growth factor-β1 on human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell growth. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(39): 6316-6324
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i39/6316.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i39.6316