Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2006; 12(38): 6142-6148
Published online Oct 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i38.6142
Published online Oct 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i38.6142
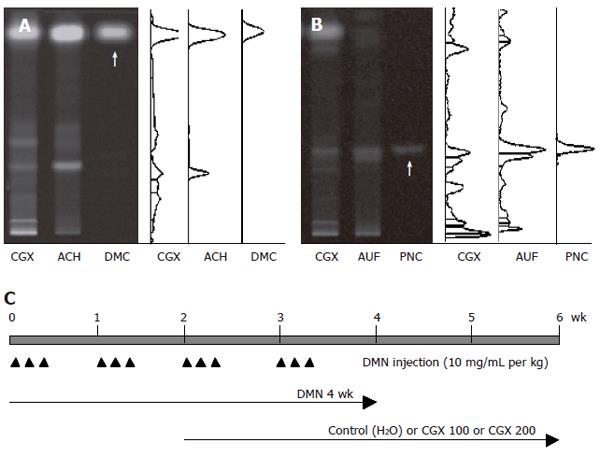
Figure 1 HPTLC-based fingerprint for CGX and scheme for the experiment.
HPTLC analysis was performed to characterize CGX and its two major components (extracts from Artemisia capillaris Herba and Aurantii Fructus) with reference components, 6,7-dimethoxycoumarin and Poncirin. A: 2 μL of CGX (200 mg/mL) and 1 μL of the extract from Artemisia capillaris Herba (50 mg/mL) were subjected to HPTLC with 1 μL of 6, 7-dimethoxycoumarin (0.1 mg/mL); B: 2 μL of CGX (200 mg/mL) and 1 μL of the extract from Aurantii Fructus (50 mg/mL) were subjected to HPTLC with 1 μL of Poncirin (5 mg/mL). Arrows indicate 6,7-dimethoxycoumarin and Poncirin, respectively; C: Simplified scheme summarizing the experimental design: DMN treatment (ip, 3 consecutive days per week, 10 mg/mL per kg for 4 wk) and CGX administration (po, 100 or 200 mg/mL per kg, for 4 wk from 2 wk after DMN treatment). ACH: Artemisia capillaris Herba; AUF: Aurantii Fructus; DMC: 6,7-dimethoxycoumarin; PNC: Poncirin.
- Citation: Shin JW, Son JY, Oh SM, Han SH, Wang JH, Cho JH, Cho CK, Yoo HS, Lee YW, Lee MM, Hu XP, Son CG. An herbal formula, CGX, exerts hepatotherapeutic effects on dimethylnitrosamine-induced chronic liver injury model in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(38): 6142-6148
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i38/6142.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i38.6142