Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2006; 12(38): 6133-6141
Published online Oct 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i38.6133
Published online Oct 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i38.6133
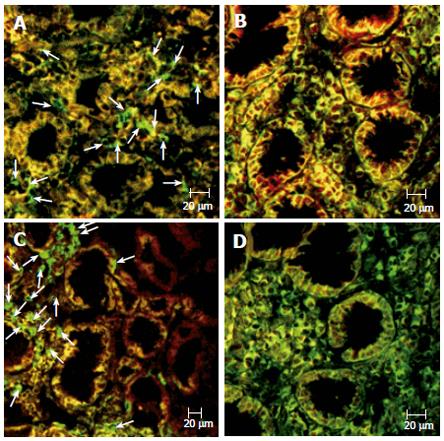
Figure 4 Double immunofluorescence analysis.
Expression of CD3 (FITC) and Fas (R-PE) in the ulcer margin of a patient with gastric ulcer (A) and a non-infected control (B). Expression of CD68 (FITC) and Fas (R-PE) in the antrum of a patient with gastric ulcer (C) and a patient with H pylori-related gastritis (D). Images obtained by confocal microscopy. Arrows show CD3 or CD68 (FITC)-single-positive cells (green) without correspondent Fas (R-PE)-positive cells in the lamina propria of the same tissue section.
-
Citation: Souza HS, Neves MS, Elia CC, Tortori CJ, Dines I, Martinusso CA, Madi K, Andrade L, Castelo-Branco MT. Distinct patterns of mucosal apoptosis in
H pylori -associated gastric ulcer are associated with altered FasL and perforin cytotoxic pathways. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(38): 6133-6141 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i38/6133.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i38.6133