Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2006; 12(38): 6133-6141
Published online Oct 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i38.6133
Published online Oct 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i38.6133
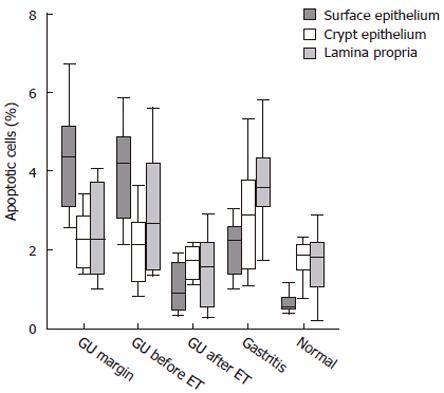
Figure 2 Percentages of apoptotic cells in the surface and crypt epithelium, and in the lamina propria of patients with gastric ulcer (GU) [at the ulcer margin, and the antrum before and after eradication therapy (ET)], H pylori-associated gastritis, and non-infected controls, respectively.
Horizontal bars represent medians, boxes represent the 25th and 75th percentiles, and vertical bars represent ranges. In the surface epithelium values were significantly different compared to GU after ET (P = 0.018; P = 0.003; P = 0.027); gastritis (P = 0.003; P = 0.002), and the control group (P < 0.001; P = 0.001). In the lamina propria values were significantly different compared to GU after ET (P = 0.001), and the control group (P = 0.001). In the crypt epithelium values were not significantly different among groups (n: GU = 12, H pylori-associated gastritis = 11, control = 10). Differences were analysed using one-way ANOVA with the Dunnett’s test for multiple comparisons. The Wilcoxon signed rank test was used for comparisons between GU patients.
-
Citation: Souza HS, Neves MS, Elia CC, Tortori CJ, Dines I, Martinusso CA, Madi K, Andrade L, Castelo-Branco MT. Distinct patterns of mucosal apoptosis in
H pylori -associated gastric ulcer are associated with altered FasL and perforin cytotoxic pathways. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(38): 6133-6141 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i38/6133.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i38.6133