Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2006; 12(37): 5978-5986
Published online Oct 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i37.5978
Published online Oct 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i37.5978
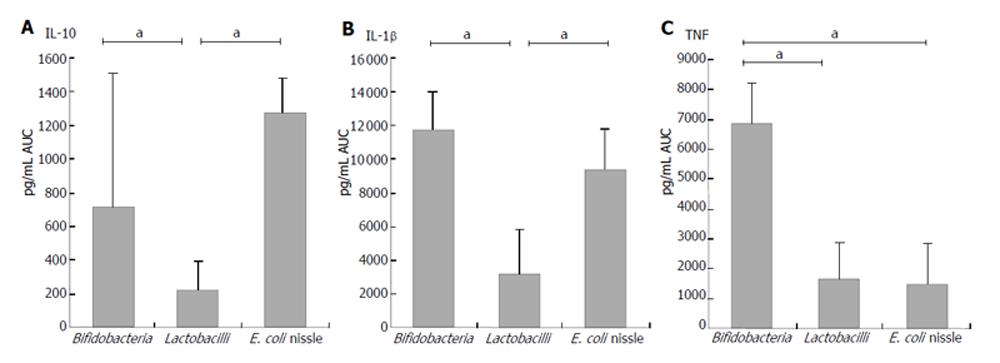
Figure 4 Supernatant concentrations of different cytokines after co-incubation of PBMNC with cell debris of bacteria from different species families.
With regard to lactobacilli results are pooled from L.acidophilus, L.bulgaricus, L.casei, L.GG, L.plantarum. With regard to bifidobacteria results are pooled from B.breve, B.infantis, B.longum. IL-10, IL-1β and TNFα shown as area under the curve (mean ± SE) ( aP < 0.05 ).
- Citation: Helwig U, Lammers KM, Rizzello F, Brigidi P, Rohleder V, Caramelli E, Gionchetti P, Schrezenmeir J, Foelsch UR, Schreiber S, Campieri M. Lactobacilli, bifidobacteria and E. coli nissle induce pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(37): 5978-5986
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i37/5978.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i37.5978